Three-dimensional spatiotemporal focusing of holographic patterns
- PMID: 27306044
- PMCID: PMC4912686
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms11928
Three-dimensional spatiotemporal focusing of holographic patterns
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Three-dimensional spatiotemporal focusing of holographic patterns.Nat Commun. 2016 Sep 2;7:12716. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12716. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27586646 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
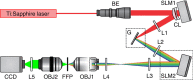
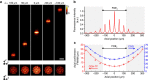
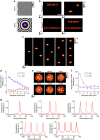
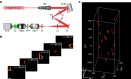
Two-photon excitation with temporally focused pulses can be combined with phase-modulation approaches, such as computer-generated holography and generalized phase contrast, to efficiently distribute light into two-dimensional, axially confined, user-defined shapes. Adding lens-phase modulations to 2D-phase holograms enables remote axial pattern displacement as well as simultaneous pattern generation in multiple distinct planes. However, the axial confinement linearly degrades with lateral shape area in previous reports where axially shifted holographic shapes were not temporally focused. Here we report an optical system using two spatial light modulators to independently control transverse- and axial-target light distribution. This approach enables simultaneous axial translation of single or multiple spatiotemporally focused patterns across the sample volume while achieving the axial confinement of temporal focusing. We use the system's capability to photoconvert tens of Kaede-expressing neurons with single-cell resolution in live zebrafish larvae.
Figures
References
-
- Denk W., Strickler J. H. & Webb W. W. Two-photon laser scanning fluorescence microscopy. Science 248, 73–76 (1990). - PubMed
-
- Salomé R. et al. Ultrafast random-access scanning in two-photon microscopy using acousto-optic deflectors. J. Neurosci. Methods 154, 161–174 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Grewe B. F., Langer D., Kasper H., Kampa B. M. & Helmchen F. High-speed in vivo calcium imaging reveals neuronal network activity with near-millisecond precision. Nat. Methods 7, 399–405 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Nguyen Q. T., Callamaras N., Hsieh C. & Parker I. Construction of a two-photon microscope for video-rate Ca2+ imaging. Cell Calcium 30, 383–393 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

