Influence of fullerene (C60) on soil bacterial communities: aqueous aggregate size and solvent co-introduction effects
- PMID: 27306076
- PMCID: PMC4910098
- DOI: 10.1038/srep28069
Influence of fullerene (C60) on soil bacterial communities: aqueous aggregate size and solvent co-introduction effects
Abstract
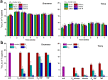
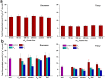
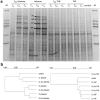
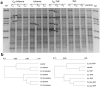
Fullerene C60 nanoparticles are being used in broad range of applications. It is important to assess their potential impacts in the environment. We evaluated the effects of C60 introduced as aqueous suspensions of nC60 aggregates of different particle size or via organic solvents on soils with different organic matter contents in this study. Impacts of the application were evaluated by measuring total microbial biomass, metabolic activity and bacterial community structure. Results show that nC60 aggregates, introduced as an aqueous suspension, had size-dependent effects on soil bacterial community composition in the low organic matter system, but induced minimal change in the microbial biomass and metabolic activity in soils with both high and low organic matter contents. Fullerene C60, co-introduced via an organic solvent, did not influence the response of soil microbes to the organic solvents. Our results suggest that nC60 aggregates of smaller size may have negative impact on soil biota and soil organic matter may play a key role in modulating the environmental effect of nanomaterials.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impact of fullerene (C60) on a soil microbial community.Environ Sci Technol. 2007 Apr 15;41(8):2985-91. doi: 10.1021/es061953l. Environ Sci Technol. 2007. PMID: 17533868
-
C60 colloid formation in aqueous systems: effects of preparation method on size, structure, and surface charge.Environ Sci Technol. 2008 Jan 1;42(1):173-8. doi: 10.1021/es071248s. Environ Sci Technol. 2008. PMID: 18350893
-
Effect of soil sorption and aquatic natural organic matter on the antibacterial activity of a fullerene water suspension.Environ Toxicol Chem. 2008 Sep;27(9):1888-94. doi: 10.1897/07-548.1. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2008. PMID: 19086207
-
Effects of C60 fullerene nanoparticles on soil bacteria and protozoans.Environ Toxicol Chem. 2008 Sep;27(9):1895-903. doi: 10.1897/07-375.1. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2008. PMID: 19086316
-
Aqueous fullerene aggregates (nC60) generate minimal reactive oxygen species and are of low toxicity in fish: a revision of previous reports.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2011 Aug;22(4):533-7. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2011.05.511. Epub 2011 Jun 28. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21719272 Review.
Cited by
-
Inactivation of Pure Bacterial Biofilms by Impaction of Aerosolized Consumer Products Containing Nanoparticulate Metals.Environ Sci Nano. 2018 Feb 1;5(2):544-555. doi: 10.1039/C7EN00972K. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Environ Sci Nano. 2018. PMID: 29755737 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon nanosol-induced assemblage of a plant-beneficial microbiome consortium.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Nov 20;21(1):436. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-02213-6. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 37986003 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in the Quantitative and Functional Characteristics of Bacterioplankton under the Influence of Aqueous Unmodified Fullerene С60 Dispersions.Dokl Biochem Biophys. 2019 Jul;487(1):256-259. doi: 10.1134/S1607672919040045. Epub 2019 Sep 26. Dokl Biochem Biophys. 2019. PMID: 31559592
-
An Androsterone-H2 @C60 hybrid: Synthesis, Properties and Molecular Docking Simulations with SARS-Cov-2.Chempluschem. 2021 Jul;86(7):972-981. doi: 10.1002/cplu.202000770. Epub 2021 Feb 4. Chempluschem. 2021. PMID: 33540487 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ma X. & Bouchard D. Formation of aqueous suspensions of fullerenes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 43, 330–336 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Baun A., Sørensen S. N., Rasmussen R. F., Hartmann N. B. & Koch C. B. Toxicity and bioaccumulation of xenobiotic organic compounds in the presence of aqueous suspensions of aggregates of nano-C60. Aquat. Toxicol. 86, 379–387 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Tao X., He Y., Fortner J. D., Chen Y. & Hughes J. B. Effects of aqueous stable fullerene nanocrystal (nC60) on copper (trace necessary nutrient metal): enhanced toxicity and accumulation of copper in Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 92, 1245–1252 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Fortner J. D. et al.. C60 in water: nanocrystal formation and microbial response. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 4307–4316 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

