Vascular CaMKII: heart and brain in your arteries
- PMID: 27306369
- PMCID: PMC5129758
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00341.2015
Vascular CaMKII: heart and brain in your arteries
Abstract
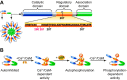
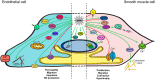
First characterized in neuronal tissues, the multifunctional calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) is a key signaling component in several mammalian biological systems. Its unique capacity to integrate various Ca(2+) signals into different specific outcomes is a precious asset to excitable and nonexcitable cells. Numerous studies have reported roles and mechanisms involving CaMKII in brain and heart tissues. However, corresponding functions in vascular cell types (endothelium and vascular smooth muscle cells) remained largely unexplored until recently. Investigation of the intracellular Ca(2+) dynamics, their impact on vascular cell function, the regulatory processes involved and more recently the spatially restricted oscillatory Ca(2+) signals and microdomains triggered significant interest towards proteins like CaMKII. Heteromultimerization of CaMKII isoforms (four isoforms and several splice variants) expands this kinase's peculiar capacity to decipher Ca(2+) signals and initiate specific signaling processes, and thus controlling cellular functions. The physiological functions that rely on CaMKII are unsurprisingly diverse, ranging from regulating contractile state and cellular proliferation to Ca(2+) homeostasis and cellular permeability. This review will focus on emerging evidence of CaMKII as an essential component of the vascular system, with a focus on the kinase isoform/splice variants and cellular system studied.
Keywords: CaMKII; calcium signaling; endothelium; vascular smooth muscle.
Copyright © 2016 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II in Vascular Smooth Muscle.Adv Pharmacol. 2017;78:171-202. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2016.08.003. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Adv Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28212797 Review.
-
CaMKII Splice Variants in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells: The Next Step or Redundancy?Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 18;23(14):7916. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147916. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CaMKII regulates intracellular Ca²⁺ dynamics in native endothelial cells.Cell Calcium. 2015 Sep;58(3):275-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2015.06.005. Epub 2015 Jun 10. Cell Calcium. 2015. PMID: 26100947
-
Cardiomyocyte calcium and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II: friends or foes?Recent Prog Horm Res. 2004;59:141-68. doi: 10.1210/rp.59.1.141. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2004. PMID: 14749501 Review.
-
CaMKIIδ and cardiomyocyte Ca(2+) signalling new perspectives on splice variant targeting.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2015 Dec;42(12):1327-32. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12489. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26361740 Review.
Cited by
-
Physiological and unappreciated roles of CaMKII in the heart.Basic Res Cardiol. 2018 Jun 15;113(4):29. doi: 10.1007/s00395-018-0688-8. Basic Res Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29905892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Kinases II and IV as Therapeutic Targets in Neurodegenerative and Neuropsychiatric Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 21;22(9):4307. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094307. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33919163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CaMKII regulates neuromuscular activity and survival of the human blood fluke Schistosoma mansoni.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 18;12(1):19831. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23962-8. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36400915 Free PMC article.
-
The Calcium Signaling Mechanisms in Arterial Smooth Muscle and Endothelial Cells.Compr Physiol. 2021 Apr 1;11(2):1831-1869. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c200030. Compr Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33792900 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial Ca2+ Signaling, Angiogenesis and Vasculogenesis: just What It Takes to Make a Blood Vessel.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 14;20(16):3962. doi: 10.3390/ijms20163962. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31416282 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aromolaran AA, Blatter LA. Modulation of intracellular Ca2+ release and capacitative Ca2+ entry by CaMKII inhibitors in bovine vascular endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 289: C1426–C1436, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Aromolaran AS, Zima AV, Blatter LA. Role of glycolytically generated ATP for CaMKII-mediated regulation of intracellular Ca2+ signaling in bovine vascular endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 293: C106–C118, 2007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

