Therapeutic progress in pediatric intracranial dural arteriovenous shunts: A review
- PMID: 27306522
- PMCID: PMC5072209
- DOI: 10.1177/1591019916653254
Therapeutic progress in pediatric intracranial dural arteriovenous shunts: A review
Abstract
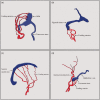
Pediatric dural arteriovenous shunts (dAVSs) are a rare form of vascular disease: Fewer than 100 cases are reported in PubMed and the understanding of pediatric dAVS is limited. For this study, we searched in PubMed, reviewed and summarized the literature related to pediatric dAVSs. Our review revealed that pediatric dAVSs have an unfavorable natural history: If left untreated, the majority of pediatric dAVSs deteriorate. In a widely accepted classification scheme developed by Lasjaunias et al., pediatric dAVSs are divided into three types: Dural sinus malformation (DMS) with dAVS, infantile dAVS (IDAVS) and adult-type dAVS (ADAVS). In general, the clinical manifestations of dAVS can be summarized as having symptoms due to high-flow arteriovenous shunts, symptoms from retrograde venous drainage, symptoms from cavernous sinus involvement and hydrocephalus, among other signs and symptoms. The pediatric dAVSs may be identified with several imaging techniques; however, the gold standard is digital subtraction angiography (DSA), which indicates unique anatomical details and hemodynamic features. Effectively treating pediatric dAVS is difficult and the prognosis is often unsatisfactory. Transarterial embolization with liquid embolic agents and coils is the treatment of choice for the safe stabilization and/or improvement of the symptoms of pediatric dAVS. In some cases, transumbilical arterial and transvenous approaches have been effective, and surgical resection is also an effective alternative in some cases. Nevertheless, pediatric dAVS can have an unsatisfactory prognosis, even when timely and appropriate treatment is administered; however, with the development of embolization materials and techniques, the potential for improved treatments and prognoses is increasing.
Keywords: Angiography; brain circulation; cerebral venous drainage; dural arteriovenous shunt; dural sinus malformation; imaging; pediatrics; procedures; review; sinus thrombosis; therapy.
© The Author(s) 2016.
Figures
References
-
- Cohen JE, Gomori JM, Benifla M, et al. Endovascular management of sigmoid sinus dural arteriovenous fistula associated with sinus stenosis in an infant. J Clin Neurosci 2013; 20: 168–170. - PubMed
-
- Lasjaunias P, Magufis G, Goulao A, et al. Anatomoclinical aspects of dural arteriovenous shunts in children. Review of 29 cases. Interv Neuroradiol 1996; 2: 179–191. - PubMed
-
- Morita A, Meyer FB, Nichols DA, et al. Childhood dural arteriovenous fistulae of the posterior dural sinuses: Three case reports and literature review. Neurosurgery 1995; 37: 1193–1199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

