Enhanced vasoconstrictor potency of the fixed combination calcipotriol plus betamethasone dipropionate in an innovative aerosol foam formulation vs. other corticosteroid psoriasis treatments
- PMID: 27306589
- PMCID: PMC5108427
- DOI: 10.1111/jdv.13714
Enhanced vasoconstrictor potency of the fixed combination calcipotriol plus betamethasone dipropionate in an innovative aerosol foam formulation vs. other corticosteroid psoriasis treatments
Abstract
Background: An aerosol foam formulation of fixed combination calcipotriol 50 μg/g (Cal) and betamethasone 0.5 mg/g (as dipropionate; BD) has been developed for psoriasis vulgaris treatment.
Objective: To compare Cal/BD aerosol foam pharmacodynamic activity with Cal/BD ointment and with other topical corticosteroids of different potencies by assessing vasoconstrictor potential.
Methods: A Phase I, single-centre, investigator-blinded, vehicle-controlled, intra-individual comparison vasoconstriction study. Healthy volunteers received a single application on selected sites of: Cal/BD aerosol foam, clobetasol propionate 0.5 mg/g cream (CP; very potent), Cal/BD ointment (potent), fluocinolone acetonide 0.25 mg/g ointment (FA; moderately potent), BD aerosol foam and aerosol foam vehicle. A seventh untreated site acted as a negative control. Skin blanching was assessed by visual (primary response criterion) and colorimetric a* and L* measurements (secondary criteria), and was analysed over time (6-32 h post-application).
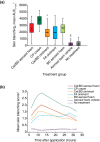
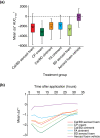
Results: Thirty-five healthy volunteers were included. All active treatments led to significantly greater skin blanching than control. By visual assessment, skin blanching with Cal/BD aerosol foam was significantly less compared with CP cream [mean AUC0-32 2560 vs. 3831; mean difference = -1272; 95% confidence interval (CI): -1598, -945; P < 0.001], similar to BD aerosol foam (mean AUC0-32 2560 vs. 2595; mean difference = -35; 95% CI: -362, 292; P = 0.83) and significantly greater than Cal/BD ointment (mean AUC0-32 2560 vs. 2008; mean difference = 552; 95% CI: 225, 878; P = 0.001) and FA ointment (mean AUC0-32 2560 vs. 1981; mean difference = 578; 95% CI: 251, 905; P < 0.001). Colorimetric assessments a* and L* also indicated significantly reduced skin blanching with Cal/BD aerosol foam compared with CP cream. No adverse events (AEs) were reported.
Conclusion: Cal/BD aerosol foam can be considered a more potent formulation than Cal/BD ointment and the moderately potent FA ointment, but less potent than the very potent corticosteroid, CP cream.
© 2016 The Authors. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Figures
References
-
- Schön MP, Boehncke W‐H. Psoriasis. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: 1899–1912. - PubMed
-
- Menter A, Korman NJ, Elmets CA et al Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Section 3. Guidelines of care for the management and treatment of psoriasis with topical therapies. J Am Acad Dermatol 2009; 60: 643–659. - PubMed
-
- Samarasekera E, Sawyer L, Parnham J, Smith CH. Assessment and management of psoriasis: summary of NICE guidance. BMJ 2012; 345: e6712. - PubMed
-
- Fleming C, Ganslandt C, Guenther L et al Calcipotriol plus betamethasone dipropionate gel compared with its active components in the same vehicle and the vehicle alone in the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris: a randomised, parallel group, double‐blind, exploratory study. Eur J Dermatol 2010; 20: 465–471. - PubMed
-
- McCormack PL. Calcipotriol/betamethasone dipropionate: a review of its use in the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris of the trunk, limbs and scalp. Drugs 2011; 71: 709–730. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

