Klebsiella pneumoniae: Going on the Offense with a Strong Defense
- PMID: 27307579
- PMCID: PMC4981674
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.00078-15
Klebsiella pneumoniae: Going on the Offense with a Strong Defense
Abstract
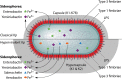
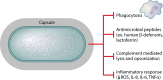
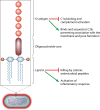
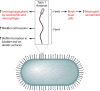
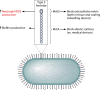
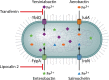
Klebsiella pneumoniae causes a wide range of infections, including pneumonias, urinary tract infections, bacteremias, and liver abscesses. Historically, K. pneumoniae has caused serious infection primarily in immunocompromised individuals, but the recent emergence and spread of hypervirulent strains have broadened the number of people susceptible to infections to include those who are healthy and immunosufficient. Furthermore, K. pneumoniae strains have become increasingly resistant to antibiotics, rendering infection by these strains very challenging to treat. The emergence of hypervirulent and antibiotic-resistant strains has driven a number of recent studies. Work has described the worldwide spread of one drug-resistant strain and a host defense axis, interleukin-17 (IL-17), that is important for controlling infection. Four factors, capsule, lipopolysaccharide, fimbriae, and siderophores, have been well studied and are important for virulence in at least one infection model. Several other factors have been less well characterized but are also important in at least one infection model. However, there is a significant amount of heterogeneity in K. pneumoniae strains, and not every factor plays the same critical role in all virulent Klebsiella strains. Recent studies have identified additional K. pneumoniae virulence factors and led to more insights about factors important for the growth of this pathogen at a variety of tissue sites. Many of these genes encode proteins that function in metabolism and the regulation of transcription. However, much work is left to be done in characterizing these newly discovered factors, understanding how infections differ between healthy and immunocompromised patients, and identifying attractive bacterial or host targets for treating these infections.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Friedlander C. 1882. Uber die scizomyceten bei der acuten fibrosen pneumonie. Arch Pathol Anat Physiol Klin Med 87:319–324.
-
- Bagley ST. 1985. Habitat association of Klebsiella species. Infect Control 6:52–58. - PubMed
-
- Rock C, Thom KA, Masnick M, Johnson JK, Harris AD, Morgan DJ. 2014. Frequency of Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC)-producing and non-KPC-producing Klebsiella species contamination of healthcare workers and the environment. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 35:426–429. doi: 10.1086/675598. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dao TT, Liebenthal D, Tran TK, Ngoc Thi Vu B, Ngoc Thi Nguyen D, Thi Tran HK, Thi Nguyen CK, Thi Vu HL, Fox A, Horby P, Van Nguyen K, Wertheim HFL. 2014. Klebsiella pneumoniae oropharyngeal carriage in rural and urban Vietnam and the effect of alcohol consumption. PLoS One 9:e91999. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091999. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

