An algorithm for computing the gene tree probability under the multispecies coalescent and its application in the inference of population tree
- PMID: 27307621
- PMCID: PMC4908345
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw261
An algorithm for computing the gene tree probability under the multispecies coalescent and its application in the inference of population tree
Abstract
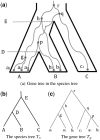
Motivation: Gene tree represents the evolutionary history of gene lineages that originate from multiple related populations. Under the multispecies coalescent model, lineages may coalesce outside the species (population) boundary. Given a species tree (with branch lengths), the gene tree probability is the probability of observing a specific gene tree topology under the multispecies coalescent model. There are two existing algorithms for computing the exact gene tree probability. The first algorithm is due to Degnan and Salter, where they enumerate all the so-called coalescent histories for the given species tree and the gene tree topology. Their algorithm runs in exponential time in the number of gene lineages in general. The second algorithm is the STELLS algorithm (2012), which is usually faster but also runs in exponential time in almost all the cases.
Results: In this article, we present a new algorithm, called CompactCH, for computing the exact gene tree probability. This new algorithm is based on the notion of compact coalescent histories: multiple coalescent histories are represented by a single compact coalescent history. The key advantage of our new algorithm is that it runs in polynomial time in the number of gene lineages if the number of populations is fixed to be a constant. The new algorithm is more efficient than the STELLS algorithm both in theory and in practice when the number of populations is small and there are multiple gene lineages from each population. As an application, we show that CompactCH can be applied in the inference of population tree (i.e. the population divergence history) from population haplotypes. Simulation results show that the CompactCH algorithm enables efficient and accurate inference of population trees with much more haplotypes than a previous approach.
Availability: The CompactCH algorithm is implemented in the STELLS software package, which is available for download at http://www.engr.uconn.edu/ywu/STELLS.html
Contact: ywu@engr.uconn.edu
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
STELLS2: fast and accurate coalescent-based maximum likelihood inference of species trees from gene tree topologies.Bioinformatics. 2017 Jun 15;33(12):1789-1797. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx079. Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 28186220
-
A coalescent-based method for population tree inference with haplotypes.Bioinformatics. 2015 Mar 1;31(5):691-8. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu710. Epub 2014 Oct 24. Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 25344500 Free PMC article.
-
Coalescent-based species tree inference from gene tree topologies under incomplete lineage sorting by maximum likelihood.Evolution. 2012 Mar;66(3):763-775. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.2011.01476.x. Epub 2011 Nov 2. Evolution. 2012. PMID: 22380439
-
Challenges in Species Tree Estimation Under the Multispecies Coalescent Model.Genetics. 2016 Dec;204(4):1353-1368. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.190173. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 27927902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Origin of land plants using the multispecies coalescent model.Trends Plant Sci. 2013 Sep;18(9):492-5. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2013.04.009. Epub 2013 May 24. Trends Plant Sci. 2013. PMID: 23707196 Review.
Cited by
-
Enumeration of compact coalescent histories for matching gene trees and species trees.J Math Biol. 2019 Jan;78(1-2):155-188. doi: 10.1007/s00285-018-1271-5. Epub 2018 Aug 16. J Math Biol. 2019. PMID: 30116881 Free PMC article.
-
ENUMERATION OF LONELY PAIRS OF GENE TREES AND SPECIES TREES BY MEANS OF ANTIPODAL CHERRIES.Adv Appl Math. 2019 Jan;102:1-17. doi: 10.1016/j.aam.2018.09.001. Epub 2018 Sep 14. Adv Appl Math. 2019. PMID: 30983650 Free PMC article.
-
Inference of population admixture network from local gene genealogies: a coalescent-based maximum likelihood approach.Bioinformatics. 2020 Jul 1;36(Suppl_1):i326-i334. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa465. Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 32657366 Free PMC article.
-
A lattice structure for ancestral configurations arising from the relationship between gene trees and species trees.Discrete Appl Math. 2024 Jan 30;343:65-81. doi: 10.1016/j.dam.2023.09.033. Epub 2023 Oct 24. Discrete Appl Math. 2024. PMID: 38078045 Free PMC article.
-
RENT+: an improved method for inferring local genealogical trees from haplotypes with recombination.Bioinformatics. 2017 Apr 1;33(7):1021-1030. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw735. Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 28065901 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Degnan J.H, Salter L.A. (2005) Gene tree distributions under the coalescent process. Evolution, 59, 24–37. - PubMed
-
- Gusfield D. (1991) Efficient algorithms for inferring evolutionary history. Networks, 21, 19–28.
-
- Hein J., Schierup M., Wiuf C. (2005) Gene Genealogies, Variation and Evolution: A Primer in Coalescent Theory. Oxford University Press, UK.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

