The Blockade of D1/D2-Like Dopamine Receptors within the Dentate Gyrus of Hippocampus Decreased the Reinstatement of Morphine-Extinguished Conditioned Place Preference in Rats
- PMID: 27307951
- PMCID: PMC4636881
The Blockade of D1/D2-Like Dopamine Receptors within the Dentate Gyrus of Hippocampus Decreased the Reinstatement of Morphine-Extinguished Conditioned Place Preference in Rats
Abstract
Introduction: The hippocampus (HIP), the primary brain structure related to learning and memory, receives sparse but comprehensive dopamine innervations and contains dopamine D1/D2-like receptors. It is demonstrated that dopamine receptors in dentate gyrus (DG) region of HIP have a remarkable function in spatial reward processing. Much less is known about the involvement of HIP and its D1/D2 dopamine receptors in drug-seeking behaviors, more particularly, in the morphine extinguished conditioned place preference (CPP).
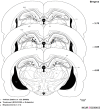
Methods: To find out the role of D1/D2-like receptors within the DG in morphine-seeking behaviors, forty adult male albino Wistar rats weighing 220-280g were unilaterally implanted by a cannula into the DG. The CPP paradigm was done; conditioning score and locomotors activity were recorded by Ethovision software. All drugs/vehicles were microinjected one day after extinction (just before the CPP test) into the DG as reinstatement day.
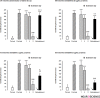
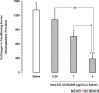
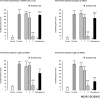
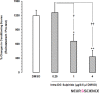
Results: The results showed that intra-DG administration of different dose of SCH23390 (0.25, 1 and 4μg/0.5μl saline), as a selective D1-like receptor antagonist and sulpiride (0.25, 1 and 4μg/0.5μl DMSO), as a selective D2-like receptor antagonist dose-dependently attenuated the morphine-extinguished CPP reinstated by priming injection of morphine (1 mg/kg;sc).
Discussion: It can be concluded that D1/D2-like receptors within this region have an important role in morphine-seeking behaviors in extinguished rats.
Keywords: D1-like receptor; D2-like receptor; Dentate gyrus; Morphine; Reinstatement; Reward.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Involvement of D1- and D2-like dopamine receptors in the dentate gyrus in the acquisition, expression, and extinction of the morphine-induced conditioned place preference in rats.Behav Brain Res. 2018 Nov 1;353:185-193. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2018.07.018. Epub 2018 Jul 24. Behav Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 30053460
-
D1- and D2-like dopamine receptors in the CA1 region of the hippocampus are involved in the acquisition and reinstatement of morphine-induced conditioned place preference.Behav Brain Res. 2016 Oct 1;312:394-404. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.06.061. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Behav Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 27374160
-
The blockade of D1- and D2-like dopamine receptors within the dentate gyrus attenuates food deprivation stress-induced reinstatement of morphine-extinguished conditioned place preference in rats.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2020 Sep;196:172967. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2020.172967. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2020. PMID: 32553787
-
Antagonism of the D1- and D2-like dopamine receptors in the nucleus accumbens attenuates forced swim stress- and morphine priming-induced reinstatement of extinguished rats.Behav Brain Res. 2018 Apr 2;341:16-25. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2017.12.010. Epub 2017 Dec 12. Behav Brain Res. 2018. PMID: 29246771
-
D1- and D2-like receptors in the dentate gyrus region of the hippocampus are involved in the reinstatement induced by a subthreshold dose of morphine and forced swim stress in extinguished morphine-CPP in rats.Behav Neurosci. 2019 Dec;133(6):545-555. doi: 10.1037/bne0000335. Epub 2019 Aug 15. Behav Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31414832
Cited by
-
Contribution of D1R-expressing neurons of the dorsal dentate gyrus and Cav1.2 channels in extinction of cocaine conditioned place preference.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2020 Aug;45(9):1506-1517. doi: 10.1038/s41386-019-0597-z. Epub 2020 Jan 6. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2020. PMID: 31905369 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamatergic Systems and Memory Mechanisms Underlying Opioid Addiction.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2021 Mar 1;11(3):a039602. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a039602. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2021. PMID: 32341068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct Regulation of Dopamine D3 Receptor in the Basolateral Amygdala and Dentate Gyrus during the Reinstatement of Cocaine CPP Induced by Drug Priming and Social Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 18;22(6):3100. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063100. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33803578 Free PMC article.
-
Common neurocircuitry mediating drug and fear relapse in preclinical models.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Jan;236(1):415-437. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-5024-3. Epub 2018 Sep 25. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30255379 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Acquas E., Carboni E., Leone P., Di Chiara G. (1989). SCH 23390 blocks drug-conditioned place-preference and place-aversion: anhedonia (lack of reward) or apathy (lack of motivation) after dopamine-receptor blockade? Psychopharmacology, 99( 2), 151–155 . - PubMed
-
- Attarzadeh-Yazdi G., Arezoomandan R., Haghparast A. (2014). Minocycline, an antibiotic with inhibitory effect on microglial activation, attenuates the maintenance and reinstatement of methamphetamine-seeking behavior in rat. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 53, 142– 148. - PubMed
-
- Cami J., Farré M. (2003). Drug addiction. New England Journal of Medicine, 349 ( 10), 975– 986. - PubMed
-
- Corrigall W. A., Linseman M. A. (1988). Conditioned place preference produced by intra-hippocampal morphine. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior, 30 ( 3), 787– 789. - PubMed
-
- De Vries T. J., Schoffelmeer A. N., Binnekade R., Raaso H., Vanderschuren L. J. (2001). Relapse to cocaine-and heroin-seeking behavior mediated by dopamine D2 receptors is time-dependent and associated with behavioral sensitization. Neuropsychopharmalogy, 26, 15– 26. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
