(3) He Spin Filter for Neutrons
- PMID: 27308139
- PMCID: PMC4849585
- DOI: 10.6028/jres.110.042
(3) He Spin Filter for Neutrons
Abstract
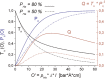
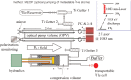
The strongly spin-dependent absorption of neutrons in nuclear spin-polarized (3)He opens up the possibility of polarizing neutrons from reactors and spallation sources over the full kinematical range of cold, thermal and hot neutrons. This paper gives a report on the neutron spin filter (NSF) development program at Mainz. The polarization technique is based on direct optical pumping of metastable (3)He atoms combined with a polarization preserving mechanical compression of the gas up to a pressure of several bar, necessary to run a NSF. The concept of a remote type of operation using detachable NSF cells is presented which requires long nuclear spin relaxation times of order 100 hours. A short survey of their use under experimental conditions, e.g. large solid-angle polarization analysis, is given. In neutron particle physics NSFs are used in precision measurements to test fundamental symmetry concepts.
Keywords: 3He polarizer and compressor; neutron spin filter; optical pumping; parity violation; polarization analysis; polarized neutrons; relaxation.
Figures






References
-
- Heil W, Andersen K, Hofmann D, Humblot H, Kulda J, Lelièvre-Berna E, Schärpf O, Tasset F. 3He neutron spin filter at ILL. Physica B. 1998;241–243:56–63.
-
- Heil W, Dreyer J, Hofmann D, Humblot H, Lelièvre-Berna E, Tasset F. 3He neutron spin-filter. Physica B. 1999;267–268:328–335.
-
- Jones GL, Gentile TR, Thompson AK, Chowdhuri Z, Dewey MS, Snow WM, Wietfeldt FE. Test of 3He-based neutron polarizers at NIST. Nucl Instr and Meth A. 2000;440:772–776.
-
- Heil W, Andersen KH, Cywinski R, Humblot H, Ritter C, Roberts TW, Stewart JR. Large solid-angle polarisation analysis at thermal neutron wavelengths using a 3He spin filter. Nucl Instr and Meth A. 2002;485:551–570.
-
- Zimmer O, Hautle P, Heil W, Hofmann D, Humblot H, Krasnoschekova I, Lasakov M, Müller TM, Neshizhevsky V, Reich J, Serebrov A, Sobolev Yu, Vassilev A. Spin filters and supermirrors: a comparison study of two methods of high-precision neutron polarisation analysis. Nucl Instr and Meth A. 2000;440:764–771.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
