Synthetic Studies on Tricyclic Diterpenoids: Direct Allylic Amination Reaction of Isopimaric Acid Derivatives
- PMID: 27308214
- PMCID: PMC4906488
- DOI: 10.1002/open.201500187
Synthetic Studies on Tricyclic Diterpenoids: Direct Allylic Amination Reaction of Isopimaric Acid Derivatives
Abstract
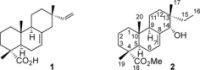
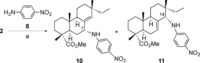
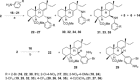
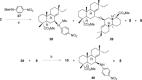
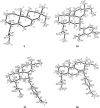
A selective synthesis of 7- or 14-nitrogen containing tricyclic diterpenoids was completed according to a strategy in which the key step was the catalyzed direct allylic amination of methyl 14α-hydroxy-15,16-dihydroisopimarate with a wide variety of nitrogenated nucleophiles. It was revealed that the selectivity of the reaction depends on the nature of nucleophile. The catalyzed reaction of the mentioned diterpenoid allylic alcohol with 3-nitroaniline, 3-(trifluoromethyl)aniline, and 4-(trifluoromethyl)aniline yield the subsequent 7α-, 7β- and 14αnitrogen-containing diterpenoids. The reaction with 2-nitroaniline, 4-nitro-2-chloroaniline, 4-methoxy-2-nitroaniline, phenylsulfamide, or tert-butyl carbamate proceeds with the formation of 7α-nitrogen-substituted diterpenoids as the main products.
Keywords: allylic amination reaction; diterpenoids; gold catalysis; pimaranes; stereoselectivity.
Figures
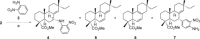
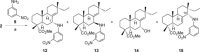
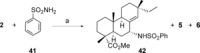
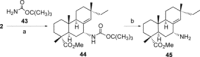
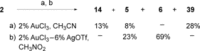
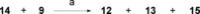
Similar articles
-
Efficient Synthesis of the N-(buta-2,3-dienyl)carboxamide of Isopimaric Acid and the Potential of This Compound towards Heterocyclic Derivatives of Diterpenoids.ChemistryOpen. 2018 Nov 14;7(11):890-901. doi: 10.1002/open.201800205. eCollection 2018 Nov. ChemistryOpen. 2018. PMID: 30460170 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of Iridium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Substitution Reactions in Target-Oriented Synthesis.Acc Chem Res. 2017 Oct 17;50(10):2539-2555. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00300. Epub 2017 Sep 22. Acc Chem Res. 2017. PMID: 28937739
-
Asymmetric Allylic Amination of Alkyl-Substituted Allylic Carbonates with Pyridones Catalyzed by the Krische Iridium Complex.Org Lett. 2024 Oct 11;26(40):8632-8635. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.4c03400. Epub 2024 Sep 27. Org Lett. 2024. PMID: 39331508
-
Synthesis of 3,4-Fused Tricyclic Indoles Using 3-Alkylidene Indolines as Versatile Precursors.Chem Rec. 2019 Feb;19(2-3):320-332. doi: 10.1002/tcr.201800043. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Chem Rec. 2019. PMID: 29931736 Review.
-
Applications of Transition-Metal-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Substitution in Total Synthesis of Natural Products: An Update.Chem Rec. 2021 Jan;21(1):29-68. doi: 10.1002/tcr.202000086. Epub 2020 Nov 18. Chem Rec. 2021. PMID: 33206466 Review.
References
-
- None
-
- Tolstikov G. A., Tolstikova T. G., Shults E. E., Tolstikov S. E., Khvostov M. V., Resin Acids from Ruissian Forest Conifers. Chemistry and Pharmacology (Ed.: B. A. Trofimov), Academic Publishing House GEO, Novosibirsk: 2011, pp. 207–242.
-
- None
-
- Smith E., E, Williamson , Zloh M., Gibbons S., Phytother. Res. 2005, 19, 538–542; - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

