Association between ideal cardiovascular health and the atherogenic index of plasma
- PMID: 27310971
- PMCID: PMC4998457
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003866
Association between ideal cardiovascular health and the atherogenic index of plasma
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Medicine, Volume 95, Issue 24: Erratum.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Aug 7;95(31):e5074. doi: 10.1097/01.md.0000490009.39850.74. eCollection 2016 Aug. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 31265618 Free PMC article.
Abstract
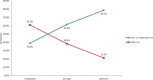
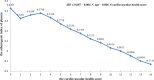
The American Heart Association aims to improve cardiovascular health by encouraging the general population to meet 7 cardiovascular health behaviors and factors. The atherogenic index of plasma (AIP) is an important index. Our aim is to evaluate the relationship between ideal cardiovascular health and the atherogenic index of plasma (AIP) in middle-aged Chinese men.A cross-sectional study was performed. A total of 27,824 middle-aged Chinese men were enrolled. The association between ideal cardiovascular health behaviors and factors and AIP was determined. The 7 cardiovascular health metrics were scored as follows: 0, poor; 1, general; and 2, ideal. The cardiovascular health status was classified according to the total score, as follows: 0 to 4, inadequate; 5 to 9, average; and 10 to 14, optimum. Analyses assessed the prevalence of 7 cardiovascular health metrics, its association with AIP. Logistic regression models were used to calculate odds ratios (ORs), adjusting for age.All 7 cardiovascular health metrics were shown to correlate with AIP (all P values < 0.05), and the strongest correlation existed between body mass and AIP, followed by total cholesterol and AIP. The mean AIP level increased with the decrease in the score of each of the 7 cardiovascular health metrics (all P values < 0.05). The subjects with poor cardiovascular health status had a 4.982-fold increase in the high risk of developing atherosclerosis, whereas a 1-point increase in the cardiovascular health score resulted a 0.046 reduction in AIP and a 22.3% reduction in the high-risk of developing atherosclerosis (OR = 0.777, 95% CI: 0.768-0.787).The ideal cardiovascular health score correlated significantly with AIP, and a 1-point increase in the cardiovascular health score led to a 0.046 reduction in AIP and a 22.3% reduction in the high risk of developing atherosclerosis. These validated the value of ideal cardiovascular health behaviors and factors in the prediction of high risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. Ideal cardiovascular health metrics are of great realistic significance for the prevention and control of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Lloyd-Jones D, Adams RJ, et al. Writing Group Members. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2010 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2010;1217:e46–215. - PubMed
-
- National Center for Cardiovascular Disease, China. Report on Cardiovascular disease in China (2013). Beijing: Encyclopedia of China Publishing House, 2014.
-
- Ford ES, Ajani UA, Croft JB, et al. Explaining the decrease in U.S. deaths from coronary disease, 1980–2000. N Engl J Med 2007;35623:2388–98. - PubMed
-
- Wu S, Huang Z, Yang X, et al. Prevalence of ideal cardiovascular health and its relationship with the 4-year cardiovascular events in a northern Chinese industrial city. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 2012;54:487–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous