Aberrant long-range functional connectivity density in generalized tonic-clonic seizures
- PMID: 27310985
- PMCID: PMC4998471
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003893
Aberrant long-range functional connectivity density in generalized tonic-clonic seizures
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Medicine, Volume 95, Issue 24: Erratum.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Aug 7;95(31):e5074. doi: 10.1097/01.md.0000490009.39850.74. eCollection 2016 Aug. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 31265618 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Studies in generalized tonic-clonic seizures (GTCS) have reported both structural and functional alterations in the brain. However, changes in spontaneous neuronal functional organization in GTCS remain largely unknown.In this study, 70 patients with idiopathic generalized epilepsy characterized by tonic-clonic seizures and 70 age- and sex-matched healthy controls were recruited. Here, functional connectivity density (FCD) mapping, an ultrafast data-driven method based on functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), was applied for the first time to investigate the changes of spontaneous functional brain activity caused by epilepsy.The results showed significantly decreased long-range FCD in the middle and inferior temporal, prefrontal, and inferior parietal cortices as well as increased long-range FCD in the cerebellum anterior lobe and sensorimotor areas. Negative correlation between duration of disease and reduced long-range FCD was found. In addition, most regions with reduced long-range FCD showed decreased resting-state functional connectivity (rsFC) within default mode network.Negative correlation between duration of disease and long-range FCD may reflect an adverse consequence eventually from original. Furthermore, the observed FCD and rsFC alterations have been speculated to be associated with the social-cognitive impairments as well as motor control. Our study provided novel evidences to look into neuro-pathophysiological mechanisms underlying GTCS.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no financial relationships relevant to this article to disclose. All authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
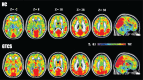



References
-
- Engel J. A proposed diagnostic scheme for people with epileptic seizures and with epilepsy: report of the ILAE Task Force on Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia 2001;42:796–803. - PubMed
-
- Bailet LL, Turk WR. The impact of childhood epilepsy on neurocognitive and behavioral performance: a prospective longitudinal study. Epilepsia 2000;41:426–31. - PubMed
-
- Hommet C, Sauerwein HC, De Toffol B, Lassonde M. Idiopathic epileptic syndromes and cognition. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2006;30:85–96. - PubMed
-
- Bernhardt BC, Rozen DA, Worsley KJ, Evans AC, et al. Thalamo–cortical network pathology in idiopathic generalized epilepsy: insights from MRI-based morphometric correlation analysis. Neuroimage 2009;46:373–81. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

