Extracellular miRNAs as biomarkers in cancer
- PMID: 27311798
- PMCID: PMC5086286
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fct.2016.06.010
Extracellular miRNAs as biomarkers in cancer
Abstract
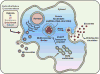
Cancer is the leading cause of death worldwide. Despite significant progress in the field leading to identification of molecular signatures of individual tumors and the development of targeted therapies, early cancer diagnosis remains a clinical challenge. The emerging era of personalized medicine has intensified research towards biomarkers that can be obtained via noninvasive means. The recent discovery of extracellular vesicles (EVs), nano-vesicles secreted by the cell, in circulation has stimulated interest in their clinical utility as cancer biomarkers. EVs are secreted from all types of cells and their contents reflect the physiological and pathological state of the cell. Multiple clinical trials are underway investigating the clinical potential of EV content to serve as biomarkers and therapeutics. However, much work remains to translate EV content into clinical application.
Keywords: Biomarker; Cancer; Clinical trial; Exosome; Extracellular vesicle; MicroRNA.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(5):E359–86. - PubMed
-
- Lopes G. Investing in cancer prevention and control to reduce global economic burden. ASCO Connection Web site; http://connection.asco.org/commentary. Updated 2016. Accessed 05/01, 2016.
-
- Dancey JE, Bedard PL, Onetto N, Hudson TJ. The genetic basis for cancer treatment decisions. Cell. 2012;148(3):409–420. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

