Protocol for the Electroencephalography Guidance of Anesthesia to Alleviate Geriatric Syndromes (ENGAGES) study: a pragmatic, randomised clinical trial
- PMID: 27311914
- PMCID: PMC4916634
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-011505
Protocol for the Electroencephalography Guidance of Anesthesia to Alleviate Geriatric Syndromes (ENGAGES) study: a pragmatic, randomised clinical trial
Erratum in
-
Correction: Protocol for the Electroencephalography Guidance of Anesthesia to Alleviate Geriatric Syndromes (ENGAGES) study: a pragmatic, randomised clinical trial.BMJ Open. 2016 Jun 27;6(6):e011505corr1. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-011505corr1. BMJ Open. 2016. PMID: 27354078 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
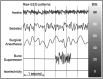
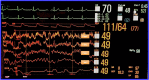
Introduction: Postoperative delirium, arbitrarily defined as occurring within 5 days of surgery, affects up to 50% of patients older than 60 after a major operation. This geriatric syndrome is associated with longer intensive care unit and hospital stay, readmission, persistent cognitive deterioration and mortality. No effective preventive methods have been identified, but preliminary evidence suggests that EEG monitoring during general anaesthesia, by facilitating reduced anaesthetic exposure and EEG suppression, might decrease incident postoperative delirium. This study hypothesises that EEG-guidance of anaesthetic administration prevents postoperative delirium and downstream sequelae, including falls and decreased quality of life.
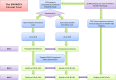
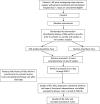
Methods and analysis: This is a 1232 patient, block-randomised, double-blinded, comparative effectiveness trial. Patients older than 60, undergoing volatile agent-based general anaesthesia for major surgery, are eligible. Patients are randomised to 1 of 2 anaesthetic approaches. One group receives general anaesthesia with clinicians blinded to EEG monitoring. The other group receives EEG-guidance of anaesthetic agent administration. The outcomes of postoperative delirium (≤5 days), falls at 1 and 12 months and health-related quality of life at 1 and 12 months will be compared between groups. Postoperative delirium is assessed with the confusion assessment method, falls with ProFaNE consensus questions and quality of life with the Veteran's RAND 12-item Health Survey. The intention-to-treat principle will be followed for all analyses. Differences between groups will be presented with 95% CIs and will be considered statistically significant at a two-sided p<0.05.
Ethics and dissemination: Electroencephalography Guidance of Anesthesia to Alleviate Geriatric Syndromes (ENGAGES) is approved by the ethics board at Washington University. Recruitment began in January 2015. Dissemination plans include presentations at scientific conferences, scientific publications, internet-based educational materials and mass media.
Trial registration number: NCT02241655; Pre-results.
Keywords: ANAESTHETICS; EDUCATION & TRAINING (see Medical Education & Training); GERIATRIC MEDICINE.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/
Figures

References
-
- Projected Future Growth of the Older Population. http://www.aoa.gov/AoARoot/Aging_Statistics/future_growth/future_growth.... – age (accessed 18 Jan 2014).
-
- Inpatient Surgery. http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/insurg.htm (accessed 18 Jan 2014).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
