Comparison of six commercial kits to extract bacterial chromosome and plasmid DNA for MiSeq sequencing
- PMID: 27312200
- PMCID: PMC4911584
- DOI: 10.1038/srep28063
Comparison of six commercial kits to extract bacterial chromosome and plasmid DNA for MiSeq sequencing
Abstract
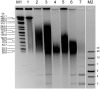
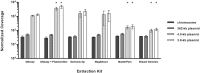
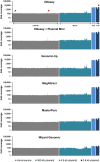
We compared commercial kits for extraction of genomic DNA from the Gram-negative bacterium Klebsiella pneumoniae for subsequent Miseq sequencing. Purification of DNA was based on matrix binding (silica or anion exchange resin) or differential precipitation (salting out), respectively. The choice of extraction kit had little effect on sequencing quality and coverage across drastically different replicons, except for an apparent depletion of small plasmids (<5 kb) during precipitation-based extractions. Sequencing coverage provided copy-number estimates for small plasmids that were consistently higher than those from quantitative real-time PCR.
Figures
References
-
- Haller S. et al. What caused the outbreak of ESBL-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in a neonatal intensive care unit, Germany 2009 to 2012? Reconstructing transmission with epidemiological analysis and whole-genome sequencing. BMJ Open 5, e007397, doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-007397 (2015). - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

