Neuroinvasion and Inflammation in Viral Central Nervous System Infections
- PMID: 27313404
- PMCID: PMC4897715
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/8562805
Neuroinvasion and Inflammation in Viral Central Nervous System Infections
Abstract
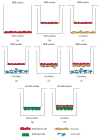
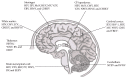
Neurotropic viruses can cause devastating central nervous system (CNS) infections, especially in young children and the elderly. The blood-brain barrier (BBB) and the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier (BCSFB) have been described as relevant sites of entry for specific viruses as well as for leukocytes, which are recruited during the proinflammatory response in the course of CNS infection. In this review, we illustrate examples of established brain barrier models, in which the specific reaction patterns of different viral families can be analyzed. Furthermore, we highlight the pathogen specific array of cytokines and chemokines involved in immunological responses in viral CNS infections. We discuss in detail the link between specific cytokines and chemokines and leukocyte migration profiles. The thorough understanding of the complex and interrelated inflammatory mechanisms as well as identifying universal mediators promoting CNS inflammation is essential for the development of new diagnostic and treatment strategies.
Figures

References
-
- Kivisäkk P., Mahad D. J., Callahan M. K., et al. Human cerebrospinal fluid central memory CD4+ T cells: evidence for trafficking through choroid plexus and meninges via P-selectin. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2003;100(14):8389–8394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1433000100. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

