Hataedock Treatment Has Preventive Therapeutic Effects in Atopic Dermatitis-Induced NC/Nga Mice under High-Fat Diet Conditions
- PMID: 27313639
- PMCID: PMC4894994
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/1739760
Hataedock Treatment Has Preventive Therapeutic Effects in Atopic Dermatitis-Induced NC/Nga Mice under High-Fat Diet Conditions
Abstract
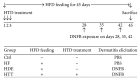
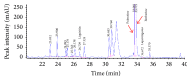
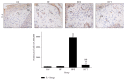
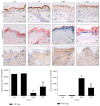
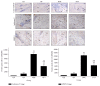
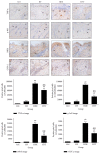
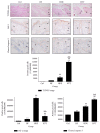
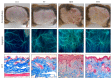
This study investigated the preventive therapeutic effects of Hataedock (HTD) treatment on inflammatory regulation and skin protection in AD-induced NC/Nga mice under high-fat diet conditions. Before inducing AD, the extract of Coptidis Rhizoma and Glycyrrhiza uralensis was administered orally to the 3-week-old mice. After that, AD-like skin lesions were induced by applying DNFB. All groups except the control group were fed a high-fat diet freely. We identified the effects of HTD on morphological changes, cytokine release and the induction of apoptosis through histochemistry, immunohistochemistry, and TUNEL assay. HTD downregulated the levels of IL-4 and PKC but increased the levels of LXR. HTD also suppressed the mast cell degranulation and release of MMP-9, Substance P. The levels of TNF-α, p-IκB, iNOS, and COX-2 were also decreased. The upregulation of inflammatory cell's apoptosis is confirmed by our results as increase of apoptotic body and cleaved caspase-3 and decrease of Bcl-2. HTD also reduced edema, angiogenesis, and skin lesion inflammation. Our results indicate HTD suppresses various inflammatory response on AD-induced mice with obesity through the regulation of Th2 differentiation and the protection of lipid barrier. Therefore, HTD could be used as an alternative and preventive therapeutic approach in the management of AD.
Figures
References
-
- Danby S., Cork M. J. A new understanding of atopic dermatitis: the role of epidermal barrier dysfunction and subclinical inflammation. Journal of Clinical Dermatology. 2012;1:33–46.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

