Ewing Sarcoma of the External Ear Canal
- PMID: 27313930
- PMCID: PMC4904079
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/6925234
Ewing Sarcoma of the External Ear Canal
Abstract
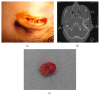
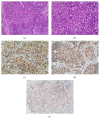
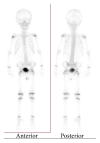
Background. Ewing sarcoma (ES) is a high-grade malignant tumor that has skeletal and extraskeletal forms and consists of small round cells. In the head and neck region, reported localization of extraskeletal ES includes the larynx, thyroid gland, submandibular gland, nasal fossa, pharynx, skin, and parotid gland, but not the external ear canal. Methods. We present the unique case of a 2-year-old boy with extraskeletal ES arising from the external ear canal, mimicking auricular hematoma. Results. Surgery was performed and a VAC/IE (vincristine, adriamycin, cyclophosphamide alternating with ifosfamide, and etoposide) regimen was used for adjuvant chemotherapy for 12 months. Conclusion. The clinician should consider extraskeletal ES when diagnosing tumors localized in the head and neck region because it may be manifested by a nonspecific clinical picture mimicking common otorhinolaryngologic disorders.
Figures
References
-
- Iriz A., Albayrak L., Eryilmaz A. Extraskeletal primary Ewing's sarcoma of the nasal cavity. International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology Extra. 2007;2(3):194–197. doi: 10.1016/j.pedex.2007.05.008. - DOI
-
- Smorenburg C. H., van Groeningen C. J., Meijer O. W. M., Visser M., Boven E. Ewing's sarcoma and primitive neuroectodermal tumours in adults: single-centre experience in the Netherlands. Netherlands Journal of Medicine. 2007;65(4):132–136. - PubMed
-
- Iezzoni J. C., Mills S. E. ‘Undifferentiated’ small round cell tumors of the sinonasal tract: differential diagnosis update. American Journal of Clinical Pathology. 2005;124:S110–S121. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

