Trisubstituted Pyrimidines as Efficacious and Fast-Acting Antimalarials
- PMID: 27314305
- PMCID: PMC4947981
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00028
Trisubstituted Pyrimidines as Efficacious and Fast-Acting Antimalarials
Abstract
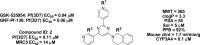
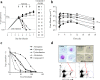
In this paper we describe the optimization of a phenotypic hit against Plasmodium falciparum, based on a trisubstituted pyrimidine scaffold. This led to compounds with good pharmacokinetics and oral activity in a P. berghei mouse model of malaria. The most promising compound (13) showed a reduction in parasitemia of 96% when dosed at 30 mg/kg orally once a day for 4 days in the P. berghei mouse model of malaria. It also demonstrated a rapid rate of clearance of the erythrocytic stage of P. falciparum in the SCID mouse model with an ED90 of 11.7 mg/kg when dosed orally. Unfortunately, the compound is a potent inhibitor of cytochrome P450 enzymes, probably due to a 4-pyridyl substituent. Nevertheless, this is a lead molecule with a potentially useful antimalarial profile, which could either be further optimized or be used for target hunting.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
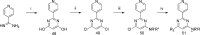

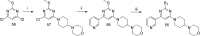
References
-
- World Health Organization. World Malaria Report 2014. World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
-
- Ariey F.; Witkowski B.; Amaratunga C.; Beghain J.; Langlois A.-C.; Khim N.; Kim S.; Duru V.; Bouchier C.; Ma L.; Lim P.; Leang R.; Duong S.; Sreng S.; Suon S.; Chuor C. M.; Bout D. M.; Menard S.; Rogers W. O.; Genton B.; Fandeur T.; Miotto O.; Ringwald P.; Le Bras J.; Berry A.; Barale J.-C.; Fairhurst R. M.; Benoit-Vical F.; Mercereau-Puijalon O.; Menard D. A molecular marker of artemisinin-resistant Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Nature 2014, 505, 50–55. 10.1038/nature12876. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Medical

