Inhibition of Advanced Glycation End-Product Formation and Antioxidant Activity by Extracts and Polyphenols from Scutellaria alpina L. and S. altissima L
- PMID: 27314314
- PMCID: PMC6273165
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules21060739
Inhibition of Advanced Glycation End-Product Formation and Antioxidant Activity by Extracts and Polyphenols from Scutellaria alpina L. and S. altissima L
Abstract
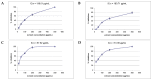
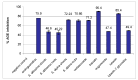
Methanolic extracts from the aerial parts and roots of two Scutellaria species, S. alpina and S. altissima, and five polyphenols from these plants demonstrated a significant ability to inhibit the formation of advanced glycation end-products (AGE) in vitro. S. alpina, which is richer in polyphenolic compounds, had strong antiglycation properties. These extracts demonstrated also high activity in the FRAP (ferric-reducing antioxidant power), antiradical (DPPH) and lipid peroxidation inhibition assays. Among the pure compounds, baicalin was the strongest glycation inhibitor (90.4% inhibition at 100 μg/mL), followed by luteolin (85.4%). Two other flavone glycosides had about half of this activity. Verbascoside was similar to the reference drug aminoguanidine (71.2% and 75.9%, respectively). The strong correlation observed between AGE inhibition and total flavonoid content indicated that flavonoids contribute significantly to antiglycation properties. A positive correlation was also observed between antiglycative and antioxidant activities. The studied skullcap species can be considered as a potential source of therapeutic agents for hyperglycemia-related disorders.
Keywords: Scutellaria alpina; Scutellaria altissima; advanced glycation end products; antioxidants; flavonoids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kaushik G., Satya S., Khandelwal R.K., Naik S.N. Commonly consumed Indian plant food materials in the management of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2010;4:21–40. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2008.02.006. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

