Early CT changes in patients admitted for thrombectomy: Intrarater and interrater agreement
- PMID: 27316243
- PMCID: PMC4955274
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002860
Early CT changes in patients admitted for thrombectomy: Intrarater and interrater agreement
Abstract
Objective: To systematically review the literature and assess agreement on the Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS) among clinicians involved in the management of thrombectomy candidates.
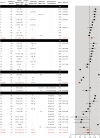
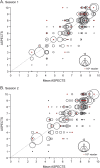
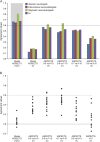
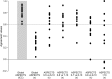
Methods: Studies assessing agreement using ASPECTS published from 2000 to 2015 were reviewed. Fifteen raters reviewed and scored the anonymized CT scans of 30 patients recruited in a local thrombectomy trial during 2 independent sessions, in order to study intrarater and interrater agreement. Agreement was measured using intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) and Fleiss kappa statistics for ASPECTS and dichotomized ASPECTS at various cutoff values.
Results: The review yielded 30 articles reporting 40 measures of agreement. Populations, methods, analyses, and results were heterogeneous (slight to excellent agreement), precluding a meta-analysis. When analyzed as a categorical variable, intrarater agreement was slight to moderate (κ = 0.042-0.469); it reached a substantial level (κ > 0.6) in 11/15 raters when the score was dichotomized (0-5 vs 6-10). The interrater ICCs varied between 0.672 and 0.811, but agreement was slight to moderate (κ = 0.129-0.315). Even in the best of cases, when ASPECTS was dichotomized as 0-5 vs 6-10, interrater agreement did not reach a substantial level (κ = 0.561), which translates into at least 5 of 15 raters not giving the same dichotomized verdict in 15% of patients.
Conclusions: In patients considered for thrombectomy, there may be insufficient agreement between clinicians for ASPECTS to be reliably used as a criterion for treatment decisions.
© 2016 American Academy of Neurology.
Figures

Comment in
-
Patient selection for stroke thrombectomy: Is CT head good enough?Neurology. 2016 Jul 19;87(3):242-3. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002872. Epub 2016 Jun 17. Neurology. 2016. PMID: 27316246 No abstract available.
References
-
- Barber PA, Demchuk AM, Zhang J, Buchan AM. Validity and reliability of a quantitative computed tomography score in predicting outcome of hyperacute stroke before thrombolytic therapy: ASPECTS Study Group: Alberta Stroke Programme Early CT Score. Lancet 2000;355:1670–1674. - PubMed
-
- Goyal M, Demchuk AM, Menon BK, et al. . Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 2015;372:1019–1030. - PubMed
-
- Jovin TG, Chamorro A, Cobo E, et al. . Thrombectomy within 8 hours after symptom onset in ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 2015;372:2296–2306. - PubMed
-
- Saver JL, Goyal M, Bonafe A, et al. . Stent-retriever thrombectomy after intravenous t-Pa vs. t-Pa alone in stroke. N Engl J Med 2015;372:2285–2295. - PubMed
-
- Berkhemer OA, Fransen PS, Beumer D, et al. . A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 2015;372:11–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
