Instituting a Low-dose CT-guided Lung Biopsy Protocol
- PMID: 27317393
- PMCID: PMC5344698
- DOI: 10.1016/j.acra.2016.05.013
Instituting a Low-dose CT-guided Lung Biopsy Protocol
Abstract
Rationale and objectives: We aimed to evaluate whether implementation of a low-dose computed tomography (CT)-guided lung biopsy protocol, with the support of individual radiologists in the section, would lead to immediate and sustained decreases in radiation dose associated with CT-guided lung biopsies.
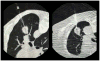
Materials and methods: A low-dose CT-guided lung biopsy protocol was developed with modifications of kilovoltage peak, milliamperes, and scan coverage. Out of 413 CT-guided lung biopsies evaluated over a 3-year period beginning in 2009, 175 performed with a standard protocol before the development of a low-dose protocol, and 238 performed with a low-dose protocol. The dose-length product (DLP) was recorded for each lung biopsy and retrospectively compared between the two protocols. Individual radiologist level DLPs were also compared before and after the protocol change.
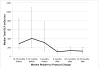
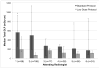
Results: The mean biopsy dose decreased by 64.4% with the low-dose protocol (113.8 milligray centimeters versus 319.7 milligray centimeters; P < 0.001). This decrease in radiation dose persisted throughout the entire 18 months evaluated following the protocol change. After the protocol change, each attending radiologist demonstrated a decrease in administered radiation dose. The diagnostic outcome rate and complication rate were unchanged over the interval.
Conclusions: Implementation of a low-dose CT-guided lung biopsy protocol resulted in an immediate reduction in patient radiation dose that was seen with all attending radiologists and persisted for at least 18 months. Such an intervention may be considered at other institutions wishing to reduce patient doses.
Keywords: CT-guided lung biopsy; Radiation dose; low-dose.
Copyright © 2016 The Association of University Radiologists. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: None
Figures
References
-
- Kalra MK, Sodickson AD, Mayo-Smith WW. CT Radiation: Key Concepts for Gentle and Wise Use. Radiographics. 2015;35:1706–1721. - PubMed
-
- Brenner DJ, Hall EJ. Computed tomography--an increasing source of radiation exposure. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:2277–2284. - PubMed
-
- Prosch H, Stadler A, Schilling M, Burklin S, Eisenhuber E, Schober E, Mostbeck G. CT fluoroscopy-guided vs. multislice CT biopsy mode-guided lung biopsies: accuracy, complications and radiation dose. Eur J Radiol. 2012;81:1029–1033. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

