RNAi Screen Identifies Novel Regulators of RNP Granules in the Caenorhabditis elegans Germ Line
- PMID: 27317775
- PMCID: PMC4978917
- DOI: 10.1534/g3.116.031559
RNAi Screen Identifies Novel Regulators of RNP Granules in the Caenorhabditis elegans Germ Line
Abstract
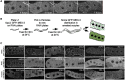
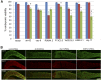
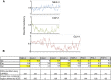
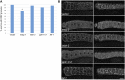
Complexes of RNA and RNA binding proteins form large-scale supramolecular structures under many cellular contexts. In Caenorhabditis elegans, small germ granules are present in the germ line that share characteristics with liquid droplets that undergo phase transitions. In meiotically-arrested oocytes of middle-aged hermaphrodites, the germ granules appear to aggregate or condense into large assemblies of RNA-binding proteins and maternal mRNAs. Prior characterization of the assembly of large-scale RNP structures via candidate approaches has identified a small number of regulators of phase transitions in the C. elegans germ line; however, the assembly, function, and regulation of these large RNP assemblies remain incompletely understood. To identify genes that promote remodeling and assembly of large RNP granules in meiotically-arrested oocytes, we performed a targeted, functional RNAi screen and identified over 300 genes that regulate the assembly of the RNA-binding protein MEX-3 into large granules. Among the most common GO classes are several categories related to RNA biology, as well as novel categories such as cell cortex, ER, and chromosome segregation. We found that arrested oocytes that fail to localize MEX-3 into cortical granules display reduced oocyte quality, consistent with the idea that the larger RNP assemblies promote oocyte quality when fertilization is delayed. Interestingly, a relatively small number of genes overlap with the regulators of germ granule assembly during normal development, or with the regulators of solid RNP granules in cgh-1 oocytes, suggesting fundamental differences in the regulation of RNP granule phase transitions during meiotic arrest.
Keywords: C. elegans; RNP granule; aging; germ line; oocyte quality.
Copyright © 2016 Wood et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biphasic adaptation to osmotic stress in the C. elegans germ line.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2017 Jun 1;312(6):C741-C748. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00364.2016. Epub 2017 Apr 5. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28381521 Free PMC article.
-
Large RNP granules in Caenorhabditis elegans oocytes have distinct phases of RNA-binding proteins.G3 (Bethesda). 2022 Aug 25;12(9):jkac173. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac173. G3 (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 35816006 Free PMC article.
-
Large P body-like RNPs form in C. elegans oocytes in response to arrested ovulation, heat shock, osmotic stress, and anoxia and are regulated by the major sperm protein pathway.Dev Biol. 2008 Jun 1;318(1):38-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.02.059. Epub 2008 Mar 14. Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18439994 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the regulation of RNP granule assembly in oocytes.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2012;295:233-89. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394306-4.00013-7. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22449492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Germ granules and gene regulation in the Caenorhabditis elegans germline.Genetics. 2022 Mar 3;220(3):iyab195. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyab195. Genetics. 2022. PMID: 35239965 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ATP-induced crosslinking of a biomolecular condensate.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 18:2023.04.18.535486. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.18.535486. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Biophys J. 2024 Jun 4;123(11):1356-1366. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2023.07.013. PMID: 37131735 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
ATP-induced cross-linking of a biomolecular condensate.Biophys J. 2024 Jun 4;123(11):1356-1366. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2023.07.013. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Biophys J. 2024. PMID: 37480229 Free PMC article.
-
Germ Cell Responses to Stress: The Role of RNP Granules.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Oct 1;7:220. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00220. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31632971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imaging-associated stress causes divergent phase transitions of RNA-binding proteins in the Caenorhabditis elegans germ line.G3 (Bethesda). 2022 Aug 25;12(9):jkac172. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac172. G3 (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 35801939 Free PMC article.
-
Stress granules: Guardians of cellular health and triggers of disease.Neural Regen Res. 2026 Feb 1;21(2):588-597. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-01196. Epub 2025 Feb 24. Neural Regen Res. 2026. PMID: 39995077 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basham S. E., Rose L. S., 2001. The Caenorhabditis elegans polarity gene ooc-5 encodes a Torsin-related protein of the AAA ATPase superfamily. Development 128(22): 4645–4656. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
