Percutaneous rotational osteotomy of the femur utilizing an intramedullary rod
- PMID: 27318670
- PMCID: PMC4960059
- DOI: 10.1007/s11751-016-0257-3
Percutaneous rotational osteotomy of the femur utilizing an intramedullary rod
Abstract
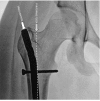
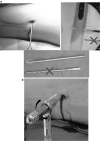
The purpose is to describe the technique and report the results and complications of percutaneous femoral rotational osteotomy, secured with a trochanteric-entry, locked intramedullary rod, in adolescents with femoral anteversion. Our series comprised an IRB approved, retrospective, consecutive series of 85 osteotomies (57 patients), followed to implant removal. The average age at surgery was 13.3 years (range 8.8-18.3) with a female-to-male ratio of 2.8:1. The minimum follow-up was 2 years. Eighty-three osteotomies healed primarily. Two patients, subsequently found to have vitamin D deficiency, broke screws and developed nonunions; both healed after repeat reaming and rod exchange and vitamin supplementation. Preoperative symptoms, including in-toeing gait, tripping and anterior knee pain or patellar instability, were resolved consistently. We did not observe significant growth disturbance or osteonecrosis. We noted a 12.5 % incidence of broken interlocking screws; this did not affect the correction or outcome except for the two patients mentioned above. This prompted a switch from a standard screw (core diameter = 3 mm) to a threaded bolt (core diameter = 3.7 mm). These results have led this technique to replace the use of plates or blade plates for rotational osteotomies.
Keywords: Anteversion; Femoral osteotomy; Intramedullary rod; Osseous necrosis; Retroversion.
Figures



References
-
- Gordon JE, Khanna N, Luhmann SJ, Dobbs MB, Ortman MR, Schoenecker PL. Intramedullary nailing of femoral fractures in children through the lateral aspect of the greater trochanter using a modified rigid humeral intramedullary nail: preliminary results of a new technique in 15 children. J Orthop Trauma. 2004;18(7):416–422. doi: 10.1097/00005131-200408000-00004. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

