Circulating Plasma microRNAs can differentiate Human Sepsis and Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS)
- PMID: 27320175
- PMCID: PMC4913253
- DOI: 10.1038/srep28006
Circulating Plasma microRNAs can differentiate Human Sepsis and Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS)
Abstract
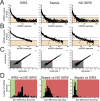
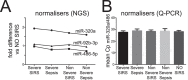
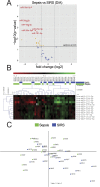
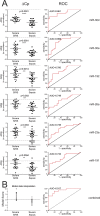
Systemic inflammation in humans may be triggered by infection, termed sepsis, or non-infective processes, termed non-infective systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). MicroRNAs regulate cellular processes including inflammation and may be detected in blood. We aimed to establish definitive proof-of-principle that circulating microRNAs are differentially affected during sepsis and non-infective SIRS. Critically ill patients with severe (n = 21) or non-severe (n = 8) intra-abdominal sepsis; severe (n = 23) or non-severe (n = 21) non-infective SIRS; or no SIRS (n = 16) were studied. Next-generation sequencing and qRT-PCR were used to measure plasma microRNAs. Detectable blood miRNAs (n = 116) were generally up-regulated in SIRS compared to no-SIRS patients. Levels of these 'circulating inflammation-related microRNAs' (CIR-miRNAs) were 2.64 (IQR: 2.10-3.29) and 1.52 (IQR: 1.15-1.92) fold higher for non-infective SIRS and sepsis respectively (p < 0.0001), hence CIR-miRNAs appeared less abundant in sepsis than in SIRS. Six CIR-miRNAs (miR-30d-5p, miR-30a-5p, miR-192-5p, miR-26a-5p, miR-23a-5p, miR-191-5p) provided good-to-excellent discrimination of severe sepsis from severe SIRS (0.742-0.917 AUC of ROC curves). CIR-miRNA levels inversely correlated with pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1, IL-6 and others). Thus, among critically ill patients, sepsis and non-infective SIRS are associated with substantial, differential changes in CIR-miRNAs. CIR-miRNAs may be regulators of inflammation and warrant thorough evaluation as diagnostic and therapeutic targets.
Conflict of interest statement
In relation to the work presented here, S.C., F.K., S.F.N. and M.J.L. declare to be inventors in a patent application submitted by the University of Sussex.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Relationship between expression of microRNA and inflammatory cytokines plasma level in pediatric patients with sepsis].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2014 Jan;52(1):28-33. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 24680405 Chinese.
-
Severity of Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome Affects the Blood Levels of Circulating Inflammatory-Relevant MicroRNAs.Front Immunol. 2018 Feb 5;8:1977. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01977. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29459855 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for serum miR-15a and miR-16 levels as biomarkers that distinguish sepsis from systemic inflammatory response syndrome in human subjects.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2012 Feb 11;50(8):1423-8. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2011-0826. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2012. PMID: 22868808
-
Role of interleukin-6 to differentiate sepsis from non-infectious systemic inflammatory response syndrome.Cytokine. 2016 Dec;88:126-135. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2016.08.033. Epub 2016 Sep 4. Cytokine. 2016. PMID: 27599258 Review.
-
Lipid profile associated with the systemic inflammatory response syndrome and sepsis in critically ill patients.Nutrition. 2018 Nov;55-56:7-14. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2018.04.007. Epub 2018 May 9. Nutrition. 2018. PMID: 29960160
Cited by
-
Sepsis Diagnostics: Intensive Care Scoring Systems Superior to MicroRNA Biomarker Testing.Diagnostics (Basel). 2020 Sep 16;10(9):701. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10090701. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32948040 Free PMC article.
-
Paving the way for precision medicine v2.0 in intensive care by profiling necroinflammation in biofluids.Cell Death Differ. 2019 Jan;26(1):83-98. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0196-2. Epub 2018 Sep 10. Cell Death Differ. 2019. PMID: 30201975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Opportunities for microRNAs in the Crowded Field of Cardiovascular Biomarkers.Annu Rev Pathol. 2019 Jan 24;14:211-238. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-012418-012827. Epub 2018 Oct 17. Annu Rev Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30332561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MEG3 Alleviated LPS-Induced Intestinal Injury in Sepsis by Modulating miR-129-5p and Surfactant Protein D.Mediators Inflamm. 2020 Jan 22;2020:8232734. doi: 10.1155/2020/8232734. eCollection 2020. Mediators Inflamm. 2020. PMID: 32410866 Free PMC article.
-
The circulatory small non-coding RNA landscape in community-acquired pneumonia on intensive care unit admission.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Aug;25(16):7621-7630. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16406. Epub 2021 Jul 17. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34272809 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine Consensus Conference: definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 20, 864–874 (1992). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

