MMP-13 is one of the critical mediators of the effect of HDAC4 deletion on the skeleton
- PMID: 27320207
- PMCID: PMC4970950
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bone.2016.06.010
MMP-13 is one of the critical mediators of the effect of HDAC4 deletion on the skeleton
Abstract
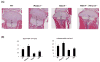
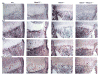
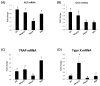
Histone deacetylase 4 (Hdac4) regulates chondrocyte hypertrophy. Hdac4(-/-) mice are runted in size and do not survive to weaning. This phenotype is primarily due to the acceleration of onset of chondrocyte hypertrophy and, as a consequence, inappropriate endochondral mineralization. Previously, we reported that Hdac4 is a repressor of matrix metalloproteinase-13 (Mmp13) transcription, and the absence of Hdac4 leads to increased expression of MMP-13 both in vitro (osteoblastic cells) and in vivo (hypertrophic chondrocytes and trabecular osteoblasts). MMP-13 is thought to be involved in endochondral ossification and bone remodeling. To identify whether the phenotype of Hdac4(-/-) mice is due to up-regulation of MMP-13, we generated Hdac4/Mmp13 double knockout mice and determined the ability of deletion of MMP-13 to rescue the Hdac4(-/-) mouse phenotype. Mmp13(-/-) mice have normal body size. Hdac4(-/-)/Mmp13(-/-) double knockout mice are significantly heavier and larger than Hdac4(-/-) mice, they survive longer, and they recover the thickness of their growth plate zones. In Hdac4(-/-)/Mmp13(-/-) double knockout mice, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) expression and TRAP-positive osteoclasts were restored (together with an increase in Mmp9 expression) but osteocalcin (OCN) was not. Micro-CT analysis of the tibiae revealed that Hdac4(-/-) mice have significantly decreased cortical bone area compared with the wild type mice. In addition, the bone architectural parameter, bone porosity, was significantly decreased in Hdac4(-/-) mice. Hdac4(-/-)/Mmp13(-/-) double knockout mice recover these cortical parameters. Likewise, Hdac4(-/-) mice exhibit significantly increased Tb.Th and bone mineral density (BMD) while the Hdac4(-/-)/Mmp13(-/-) mice significantly recovered these parameters toward normal for this age. Taken together, our findings indicate that the phenotype seen in the Hdac4(-/-) mice is partially derived from elevation in MMP-13 and may be due to a bone remodeling disorder caused by overexpression of this enzyme.
Keywords: Cortical bone; Hdac4; Hdac4(−/−)/Mmp13(−/−) double knockout; Mmp13.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
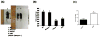




Similar articles
-
The Deletion of Hdac4 in Mouse Osteoblasts Influences Both Catabolic and Anabolic Effects in Bone.J Bone Miner Res. 2018 Jul;33(7):1362-1375. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3422. Epub 2018 Apr 25. J Bone Miner Res. 2018. PMID: 29544022 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase 4 deletion results in abnormal chondrocyte hypertrophy and premature ossification from collagen type 2α1‑expressing cells.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Nov;22(5):4031-4040. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11465. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 33000215 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-381 Regulates Chondrocyte Hypertrophy by Inhibiting Histone Deacetylase 4 Expression.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Aug 23;17(9):1377. doi: 10.3390/ijms17091377. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27563877 Free PMC article.
-
The role of histone deacetylase 4 during chondrocyte hypertrophy and endochondral bone development.Bone Joint Res. 2020 May 16;9(2):82-89. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.92.BJR-2019-0172.R1. eCollection 2020 Feb. Bone Joint Res. 2020. PMID: 32435460 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-13: A special focus on its regulation by signaling cascades and microRNAs in bone.Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 Apr 1;109:338-349. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.12.091. Epub 2017 Dec 19. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018. PMID: 29273522 Review.
Cited by
-
The Deletion of Hdac4 in Mouse Osteoblasts Influences Both Catabolic and Anabolic Effects in Bone.J Bone Miner Res. 2018 Jul;33(7):1362-1375. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3422. Epub 2018 Apr 25. J Bone Miner Res. 2018. PMID: 29544022 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances of Osterix Transcription Factor in Osteoblast Differentiation and Bone Formation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Dec 15;8:601224. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.601224. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33384998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of histone deacetylases in bone development and skeletal disorders.Bone. 2021 Feb;143:115606. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2020.115606. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Bone. 2021. PMID: 32829038 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC4 in cancer: A multitasking platform to drive not only epigenetic modifications.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Jan 24;10:1116660. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1116660. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36762207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of histone methyltransferase Ezh2 stimulates an osteogenic transcriptional program in chondrocytes but does not affect cartilage development.J Biol Chem. 2018 Dec 7;293(49):19001-19011. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003909. Epub 2018 Oct 16. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30327434 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vega RB, Matsuda K, Oh J, Barbosa AC, Yang X, Meadow E, McAnally J, Pomajzl C, Shelton JM, Richardson JA, Karsenty G, Olson EN. Histone deacetylase 4 controls chondrocyte hypertrophy during skeletogenesis. Cell. 2004;119:555–566. - PubMed
-
- Colnot CI, Helms JA. A molecular analysis of matrix remodeling and angiogenesis during long bone development. Mech Develop. 2001;100:245–250. - PubMed
-
- Maes C, Carmeliet P, Moermans K, Stockmans I, Smert N, Collen D, Bouillon R, Carmeliet G. Impaired angiogenesis and endochondral bone formation in mice lacking the vascular endothelial growth factor isoforms VEGF164 and VEGF188. Mech. Develop. 2002;111:61–73. - PubMed
-
- Zelzer E, Mamluck R, Ferrara N, Johnson RS, Schipani E, Olson BR. VEGFA is necessary for chondrocyte survival during bone development. Development and disease. 2004;131:2161–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

