The right central amygdala shows greater activation in response to an auditory conditioned stimulus in male rats
- PMID: 27320818
- PMCID: PMC5095625
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.16-0255
The right central amygdala shows greater activation in response to an auditory conditioned stimulus in male rats
Abstract
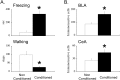
Pavlovian fear conditioning is an experimental procedure in which a conditioned stimulus (CS) acquires an ability to elicit fear responses. This type of conditioning depends on the basolateral complex of the amygdala (BLA) and/or central amygdala (CeA). We previously found that rats showed reduced fear responses to an auditory CS when they were subjected to a pre-training chemical lesion of the entire right amygdala as compared with the left amygdala. Based on this finding, we hypothesize that the BLA and/or CeA in the right hemisphere will be more strongly activated by an auditory CS than those in the left hemisphere. To test this hypothesis, we re-exposed fear-conditioned and non-conditioned rats to an auditory CS 1 day after fear conditioning. We assessed Fos expression in the BLA and CeA in each hemisphere. We found that fear-conditioned subjects showed fear responses, such as increased freezing and decreased walking, as well as increased Fos expression in the BLA and CeA. When we compared Fos expression between hemispheres, Fos expression in the CeA, but not the BLA, was greater in the right hemisphere compared with the left hemisphere. These results suggest that the right CeA is more strongly activated by the auditory CS.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

