The epidemiology and clinical features of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in neonates
- PMID: 27320858
- PMCID: PMC9427572
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjid.2016.04.008
The epidemiology and clinical features of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in neonates
Abstract
Objectives: This retrospective study was aimed to explore the epidemiological and clinical profiles of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in neonates.
Methods: From 2011 to 2014, 1322 hospitalized neonates with lower respiratory tract infections were screened for Mycoplasma pneumoniae by detection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae antibodies using Serion ELISA classic Mycoplasma pneumoniae kits.
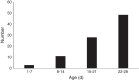
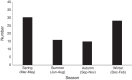
Results: Mycoplasma pneumoniae was identified in 89 (6.7%) patients. The age ranged from 1 day to 28 days with a median of 22 days. The male to female ratio was 1.15:1. Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection peaked in spring (from March through May) and winter (from December through February). Compared with non-Mycoplasma pneumoniae infected neonates, those with Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection were older, presented fever more frequently, and had less tachypnea.
Conclusions: Mycoplasma pneumoniae could be an important etiologic agent for respiratory tract infection in neonates. In neonates Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection was usually associated with older age, presence of fever, and less tachypnea. Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in neonates tends to be a mild process.
Keywords: Lower respiratory tract infection; Mycoplasma pneumoniae; Neonate.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence of Mycoplasma pneumoniae-associated respiratory tract infections in hospitalized children: results of a 4-year prospective study in Tunis.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010 Oct;68(2):103-9. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2010.05.010. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20846581
-
Prevalence of Mycoplasma IgM in children with lower respiratory tract illness.Pediatr Int. 2009 Oct;51(5):684-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-200X.2009.02858.x. Epub 2009 Mar 24. Pediatr Int. 2009. PMID: 19419518
-
[Seroprevalence of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in Poland in 2008-2013].Med Dosw Mikrobiol. 2014;66(2):105-14. Med Dosw Mikrobiol. 2014. PMID: 25369657 Polish.
-
Acute respiratory infection due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae: current status of diagnostic methods.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010 Sep;29(9):1055-69. doi: 10.1007/s10096-010-0975-2. Epub 2010 Jun 6. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20526788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae: its role in respiratory infection.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013 Mar;68(3):506-11. doi: 10.1093/jac/dks457. Epub 2012 Nov 20. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23169891 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of miR-29c/B7-H3/Th17 axis in children with Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia.Ital J Pediatr. 2019 May 14;45(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s13052-019-0655-5. Ital J Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31088519 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with indirect immunofluorescence assay for the diagnosis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection.J Clin Lab Anal. 2019 Feb;33(2):e22677. doi: 10.1002/jcla.22677. Epub 2018 Sep 17. J Clin Lab Anal. 2019. PMID: 30221425 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of serodiagnosis methods for community-acquired Mycoplasma pneumoniae respiratory tract infections in children.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Jul 21;102(29):e34133. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034133. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37478238 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal meconium aspiration syndrome associated with ABCA3 gene mutation and mycoplasma infection: a case report.BMC Pediatr. 2025 Jan 9;25(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12887-024-05369-8. BMC Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 39789505 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of doxycycline for severe Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in pediatric patients.Clin Exp Med. 2025 Jul 22;25(1):259. doi: 10.1007/s10238-025-01793-x. Clin Exp Med. 2025. PMID: 40694196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee K.Y. Pediatric respiratory infections by Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2008;6:509–521. - PubMed
-
- He X.Y., Wang X.B., Zhang R., et al. Investigation of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in pediatric population from 12,025 cases with respiratory infection. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013;75:22–27. - PubMed
-
- Sun H., Chen Z., Yan Y., Huang L., Wang M., Ji W. Epidemiology and clinical profiles of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in hospitalized infants younger than one year. Respir Med. 2015;109:751–757. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources