RBPJ maintains brain tumor-initiating cells through CDK9-mediated transcriptional elongation
- PMID: 27322055
- PMCID: PMC4922685
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI86114
RBPJ maintains brain tumor-initiating cells through CDK9-mediated transcriptional elongation
Abstract
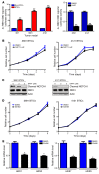
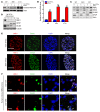
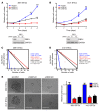
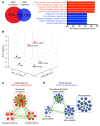
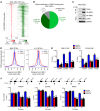
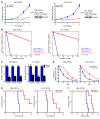
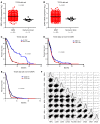
Glioblastomas co-opt stem cell regulatory pathways to maintain brain tumor-initiating cells (BTICs), also known as cancer stem cells. NOTCH signaling has been a molecular target in BTICs, but NOTCH antagonists have demonstrated limited efficacy in clinical trials. Recombining binding protein suppressor of hairless (RBPJ) is considered a central transcriptional mediator of NOTCH activity. Here, we report that pharmacologic NOTCH inhibitors were less effective than targeting RBPJ in suppressing tumor growth. While NOTCH inhibitors decreased canonical NOTCH gene expression, RBPJ regulated a distinct profile of genes critical to BTIC stemness and cell cycle progression. RBPJ was preferentially expressed by BTICs and required for BTIC self-renewal and tumor growth. MYC, a key BTIC regulator, bound the RBPJ promoter and treatment with a bromodomain and extraterminal domain (BET) family bromodomain inhibitor decreased MYC and RBPJ expression. Proteomic studies demonstrated that RBPJ binds CDK9, a component of positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb), to target gene promoters, enhancing transcriptional elongation. Collectively, RBPJ links MYC and transcriptional control through CDK9, providing potential nodes of fragility for therapeutic intervention, potentially distinct from NOTCH.
Figures


Comment in
-
γ-Secretase inhibitor-resistant glioblastoma stem cells require RBPJ to propagate.J Clin Invest. 2016 Jul 1;126(7):2415-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI88619. Epub 2016 Jun 20. J Clin Invest. 2016. PMID: 27322058 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U54 HG006991/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA169117/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS070315/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA198892/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA171652/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS089272/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS087913/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA197718/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007250/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA154130/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F30 CA203101/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute /International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

