Antibacterial Activity of Juglone against Staphylococcus aureus: From Apparent to Proteomic
- PMID: 27322260
- PMCID: PMC4926497
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17060965
Antibacterial Activity of Juglone against Staphylococcus aureus: From Apparent to Proteomic
Abstract
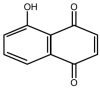
The proportion of foodborne disease caused by pathogenic microorganisms is rising worldwide, with staphylococcal food poisoning being one of the main causes of this increase. Juglone is a plant-derived 1,4-naphthoquinone with confirmed antibacterial and antitumor activities. However, the specific mechanism underlying its antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus remains unclear. To elucidate the mechanism underlying its antibacterial activity, isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation methods of quantitative proteomics were applied for analysis of the 53 proteins that were differentially expressed after treatment with juglone. Combined with verification experiments, such as detection of changes in DNA and RNA content and quantification of oxidative damage, our results suggested that juglone effectively increased the protein expression of oxidoreductase and created a peroxidative environment within the cell, significantly reducing cell wall formation and increasing membrane permeability. We hypothesize that juglone binds to DNA and reduces DNA transcription and replication directly. This is the first study to adopt a proteomic approach to investigate the antibacterial mechanism of juglone.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; antibacterial activity; iTRAQ; juglone.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Proteomic Analysis of the Antibacterial Mechanism of Action of Juglone against Staphylococcus aureus.Nat Prod Commun. 2016 Jun;11(6):825-7. Nat Prod Commun. 2016. PMID: 27534127
-
Antibacterial mechanism of daptomycin antibiotic against Staphylococcus aureus based on a quantitative bacterial proteome analysis.J Proteomics. 2017 Jan 6;150:242-251. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2016.09.014. Epub 2016 Sep 29. J Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 27693894
-
Antibacterial Activity of Juglone Revealed in a Wound Model of Staphylococcus aureus Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 15;24(4):3931. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043931. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835350 Free PMC article.
-
An overview on the antibacterial properties of juglone, naphthazarin, plumbagin and lawsone derivatives and their metal complexes.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Jun;162:114690. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114690. Epub 2023 Apr 17. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37075666 Review.
-
FtsZ inhibition: a promising approach for antistaphylococcal therapy.Drug News Perspect. 2010 Jun;23(5):295-304. doi: 10.1358/dnp.2010.23.5.1429489. Drug News Perspect. 2010. PMID: 20603653 Review.
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Antibacterial Mechanism of Limonene against Listeria monocytogenes.Molecules. 2019 Dec 20;25(1):33. doi: 10.3390/molecules25010033. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31861877 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, Structure Elucidation, Antibacterial Activities, and Synergistic Effects of Novel Juglone and Naphthazarin Derivatives Against Clinical Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strains.Front Chem. 2021 Nov 19;9:773981. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.773981. eCollection 2021. Front Chem. 2021. PMID: 34869221 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the Mechanism of Formation of a Response to Juglone for Intact and Immobilized Bacterial Cells as Recognition Elements of Microbial Sensors: Processes Causing the Biosensor Response.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 Feb 21;11(2):56. doi: 10.3390/bios11020056. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33669923 Free PMC article.
-
Novel 2-Amino-1,4-Naphthoquinone Derivatives Induce A549 Cell Death through Autophagy.Molecules. 2023 Apr 7;28(8):3289. doi: 10.3390/molecules28083289. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37110525 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of 1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives as antibacterial agents: activity and mechanistic studies.Front Environ Sci Eng. 2023;17(3):31. doi: 10.1007/s11783-023-1631-2. Epub 2022 Oct 20. Front Environ Sci Eng. 2023. PMID: 36313056 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

