HTLV-1 Infection and Adult T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma-A Tale of Two Proteins: Tax and HBZ
- PMID: 27322308
- PMCID: PMC4926181
- DOI: 10.3390/v8060161
HTLV-1 Infection and Adult T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma-A Tale of Two Proteins: Tax and HBZ
Abstract
HTLV-1 (Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1) is a complex human delta retrovirus that currently infects 10-20 million people worldwide. While HTLV-1 infection is generally asymptomatic, 3%-5% of infected individuals develop a highly malignant and intractable T-cell neoplasm known as adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATL) decades after infection. How HTLV-1 infection progresses to ATL is not well understood. Two viral regulatory proteins, Tax and HTLV-1 basic zipper protein (HBZ), encoded by the sense and antisense viral transcripts, respectively, are thought to play indispensable roles in the oncogenic process of ATL. This review focuses on the roles of Tax and HBZ in viral replication, persistence, and oncogenesis. Special emphasis is directed towards recent literature on the mechanisms of action of these two proteins and the roles of Tax and HBZ in influencing the outcomes of HTLV-1 infection including senescence induction, viral latency and persistence, genome instability, cell proliferation, and ATL development. Attempts are made to integrate results from cell-based studies of HTLV-1 infection and studies of HTLV-1 proviral integration site preference, clonality, and clonal expansion based on high throughput DNA sequencing. Recent data showing that Tax hijacks key mediators of DNA double-strand break repair signaling-the ubiquitin E3 ligase, ring finger protein 8 (RNF8) and the ubiquitin E2 conjugating enzyme (UBC13)-to activate the canonical nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B-cells (NF-κB) and other signaling pathways will be discussed. A perspective on how the Tax-RNF8 signaling axis might impact genomic instability and how Tax may collaborate with HBZ to drive oncogenesis is provided.
Keywords: DNA damage response; HTLV-1; K63-linked polyubiquitin; RNF8; UBC13; adult T-cell leukemia; genomic instability; latency and persistence; senescence.
Figures
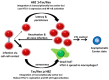
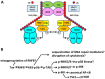
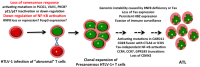
Similar articles
-
The Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1 Basic Leucine Zipper Factor Attenuates Repair of Double-Stranded DNA Breaks via Nonhomologous End Joining.J Virol. 2018 Jul 17;92(15):e00672-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00672-18. Print 2018 Aug 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29769340 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Interactions between the Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1 Antisense Protein HBZ and the SWI/SNF Chromatin Remodeling Family: Implications for Viral Life Cycle.J Virol. 2019 Jul 30;93(16):e00412-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00412-19. Print 2019 Aug 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31142665 Free PMC article.
-
Adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma as a viral disease: Subtypes based on viral aspects.Cancer Sci. 2021 May;112(5):1688-1694. doi: 10.1111/cas.14869. Epub 2021 Mar 30. Cancer Sci. 2021. PMID: 33630351 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax oncoprotein represses the expression of the BCL11B tumor suppressor in T-cells.Cancer Sci. 2015 Apr;106(4):461-5. doi: 10.1111/cas.12618. Epub 2015 Mar 16. Cancer Sci. 2015. PMID: 25613934 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted functions and roles of HBZ in HTLV-1 pathogenesis.Retrovirology. 2016 Mar 15;13:16. doi: 10.1186/s12977-016-0249-x. Retrovirology. 2016. PMID: 26979059 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of the CDK7 Gene, Coding for the Catalytic Subunit of the Cyclin-Dependent Kinase (CDK)-Activating Kinase (CAK) and General Transcription Factor II H, by the Trans-Activator Protein Tax of Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type-1.Genes (Basel). 2024 Aug 15;15(8):1080. doi: 10.3390/genes15081080. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202439 Free PMC article.
-
HTLV-1: A real pathogen or a runaway guest of a diseased cell?J Biosci. 2018 Sep;43(4):785-795. J Biosci. 2018. PMID: 30207322 Review.
-
The Past, Present, and Future of a Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1 Vaccine.Front Microbiol. 2022 May 4;13:897346. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.897346. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35602078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NF-κB signaling mechanisms in HTLV-1-induced adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma.FEBS J. 2018 Sep;285(18):3324-3336. doi: 10.1111/febs.14492. Epub 2018 May 14. FEBS J. 2018. PMID: 29722927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical and Public Health Implications of Human T-Lymphotropic Virus Type 1 Infection.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2022 Apr 20;35(2):e0007821. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00078-21. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2022. PMID: 35195446 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tsukasaki K., Hermine O., Bazarbachi A., Ratner L., Ramos J.C., Harrington W., Jr., O’Mahony D., Janik J.E., Bittencourt A.L., Taylor G.P., et al. Definition, prognostic factors, treatment, and response criteria of adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma: A proposal from an international consensus meeting. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009;27:453–459. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.18.2428. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

