Checkpoint inhibitors and other novel immunotherapies for advanced renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 27324121
- PMCID: PMC5532875
- DOI: 10.1038/nrurol.2016.103
Checkpoint inhibitors and other novel immunotherapies for advanced renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
The management of advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) has dramatically changed over the past decade. Therapies that target the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathways have considerably expanded treatment options; however, most patients with advanced RCC still have limited overall survival. Increased understanding of the mechanisms of T cell-antigen recognition and function has led to the development of novel immunotherapies to treat cancer, chief among them inhibitors of checkpoint receptors - molecules whose function is to restrain the host immune response. In 2015, the FDA approved the first checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab for patients with advanced RCC following treatment with antiangiogenic therapy based on improved overall survival compared with the standard of care. Ongoing phase III trials are comparing checkpoint-inhibitor-based combination regimens with antiangiogenesis agents in the first-line setting. The field is evolving rapidly, with many clinical trials already testing several checkpoint inhibitors alone, in combination, or with other targeted therapies. In addition, different novel immune therapies are being investigated including vaccines, T-cell agonists, and chimeric antigen receptor T cells. Determining which patients will benefit from these therapies and which combination approaches will result in better response will be important as this field evolves.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
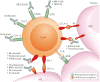

References
-
- Coley W. The treatment of malignant tumors by repeated inoculations of erysipelas: with a report of ten original cases. Am J Med Sci. 1893;105:487–510. - PubMed
-
- McDermott DF. Immunotherapy of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2009;115:2298–2305. - PubMed
-
- Fyfe G, et al. Results of treatment of 255 patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who received high-dose recombinant interleukin-2 therapy. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13:688–696. - PubMed
-
- Motzer RJ, et al. Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:115–124. - PubMed
-
- Hudes G, et al. Temsirolimus, interferon alfa, or both for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:2271–2281. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

