Dermographism in the Oral Cavity
- PMID: 27324161
- PMCID: PMC4917076
- DOI: 10.12659/ajcr.898247
Dermographism in the Oral Cavity
Abstract
Background: Dermographism is a type of physical urticaria that can be induced by writing on the skin. It occurs in 2-5% of the population and is considered to be a normal physiological phenomenon. However, in a small subset of patients, it can be symptomatic and may affect the quality of life. The etiology of this disease remains unclear.
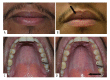
Case report: Herein, we present a case of dermographism in a 20-year-old male and discuss the involvement of the oral mucosa in this condition.
Conclusions: Although this condition is well known to occur in the skin, we believe this condition is rarely discussed among dentists. All healthcare providers, especially dentists, should know its potential to cause complications during dental procedures.
Figures

References
-
- Abajian M, Młynek A, Maurer M. Physical urticaria. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2012;12:281–87. - PubMed
-
- Wong RC, Fairley JA, Ellis JA, Arbor A. Clinical review dermographism: A review. J Am Acad Dermatology. 1984;11:1076–81. - PubMed
-
- Schoepke N, Młynek A, Weller K, et al. Symptomatic dermographism: An inadequately described disease. J Eur Acad Dermatology Venereol. 2015;29:708–12. - PubMed
-
- Mlynek A, Vieira dos Santos R, Ardelean E, et al. A novel, simple, validated and reproducible instrument for assessing provocation threshold levels in patients with symptomatic dermographism. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2013;38:360–66. - PubMed
-
- Taşkapan O, Harmanyeri Y. Evaluation of patients with symptomatic dermographism. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006;20:58–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

