Simple Factors Associated With Radiation-Induced Lung Toxicity After Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy of the Thorax: A Pooled Analysis of 88 Studies
- PMID: 27325482
- PMCID: PMC5541363
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.03.024
Simple Factors Associated With Radiation-Induced Lung Toxicity After Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy of the Thorax: A Pooled Analysis of 88 Studies
Abstract
Purpose: To study the risk factors for radiation-induced lung toxicity (RILT) after stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) of the thorax.
Methods and materials: Published studies on lung toxicity in patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) or metastatic lung tumors treated with SBRT were pooled and analyzed. The primary endpoint was RILT, including pneumonitis and fibrosis. Data of RILT and risk factors were extracted from each study, and rates of grade 2 to 5 (G2+) and grade 3 to 5 (G3+) RILT were computed. Patient, tumor, and dosimetric factors were analyzed for their correlation with RILT.
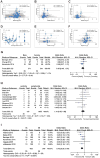
Results: Eighty-eight studies (7752 patients) that reported RILT incidence were eligible. The pooled rates of G2+ and G3+ RILT from all 88 studies were 9.1% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 7.15-11.4) and 1.8% (95% CI: 1.3-2.5), respectively. The median of median tumor sizes was 2.3 (range, 1.4-4.1) cm. Among the factors analyzed, older patient age (P=.044) and larger tumor size (the greatest diameter) were significantly correlated with higher rates of G2+ (P=.049) and G3+ RILT (P=.001). Patients with stage IA versus stage IB NSCLC had significantly lower risks of G2+ RILT (8.3% vs 17.1%, odds ratio = 0.43, 95% CI: 0.29-0.64, P<.0001). Among studies that provided detailed dosimetric data, the pooled analysis demonstrated a significantly higher mean lung dose (MLD) (P=.027) and V20 (P=.019) in patients with G2+ RILT than in those with grade 0 to 1 RILT.
Conclusions: The overall rate of RILT is relatively low after thoracic SBRT. Older age and larger tumor size are significant adverse risk factors for RILT. Lung dosimetry, specifically lung V20 and MLD, also significantly affect RILT risk.
Copyright © 2016. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

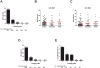

References
-
- Baumann P, Nyman J, Hoyer M, et al. Outcome in a prospective phase II trial of medically inoperable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3290–3296. - PubMed
-
- Zheng X, Schipper M, Kidwell K, et al. Survival outcome after stereotactic body radiation therapy and surgery for stage I non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014;90:603–611. - PubMed
-
- Oh D, Ahn YC, Seo JM, et al. Potentially curative stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for single or oligometastasis to the lung. Acta Oncol. 2012;51:596–602. - PubMed
-
- Tree AC, Khoo VS, Eeles RA, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for oligometastases. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:e28–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

