Immune checkpoint blockade therapy for bladder cancer treatment
- PMID: 27326412
- PMCID: PMC4910761
- DOI: 10.4111/icu.2016.57.S1.S98
Immune checkpoint blockade therapy for bladder cancer treatment
Abstract
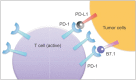
Bladder cancer remains the most immunogenic and expensive malignant tumor in the United States today. As the 4th leading cause of death from cancer in United States, Immunotherapy blocking immune checkpoints have been recently been applied to many aggressive cancers and changed interventions of urological cancers including advanced bladder cancer. The applied inhibition of PD-1-PD-L1 interactions can restore antitumor T-cell activity and enhance the cellular immune attack on antigens. The overall goals of this short review article are to introduce current cancer immunotherapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors, and to provide new insight into the underlying mechanisms that block immune checkpoints in tumor microenvironment. Furthermore, this review will address the preclinical and clinical trials to determine whether bladder cancer patients could benefit from this new cancer therapy in near future.
Keywords: Bladder cancer; Immune checkpoint; Immune therapy; PD-1; PD-L1.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bladder cancer, a unique model to understand cancer immunity and develop immunotherapy approaches.J Pathol. 2019 Oct;249(2):151-165. doi: 10.1002/path.5306. Epub 2019 Jun 24. J Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31102277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Next Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors: PD-1/PD-L1 Blockade in Melanoma.Clin Ther. 2015 Apr 1;37(4):764-82. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.02.018. Epub 2015 Mar 29. Clin Ther. 2015. PMID: 25823918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of the PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint in bladder cancer: From mediator of immune escape to target for treatment.Urol Oncol. 2017 Jan;35(1):14-20. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2016.10.004. Epub 2016 Nov 3. Urol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27816403 Review.
-
Emerging role of immunotherapy in urothelial carcinoma-Immunobiology/biomarkers.Urol Oncol. 2016 Dec;34(12):556-565. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2016.10.006. Epub 2016 Nov 9. Urol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27836246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review on the evolution of PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy for bladder cancer: The future is now.Cancer Treat Rev. 2017 Mar;54:58-67. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2017.01.007. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Cancer Treat Rev. 2017. PMID: 28214651 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanoparticles: augmenting tumor antigen presentation for vaccine and immunotherapy treatments of cancer.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2017 Dec;12(23):2693-2706. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2017-0254. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2017. PMID: 29098928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic value of immune cell infiltration in bladder cancer: A gene expression-based study.Oncol Lett. 2020 Aug;20(2):1677-1684. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11750. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32724410 Free PMC article.
-
Study on Molecular Information Intelligent Diagnosis and Treatment of Bladder Cancer on Pathological Tissue Image.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 3;9:838182. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.838182. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35755066 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Checkpoint Inhibitor Expression Directly on Exfoliated Cells from Bladder Cancer: A Narrative Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Oct 3;13(19):3119. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13193119. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinformatics Analysis Finds Immune Gene Markers Related to the Prognosis of Bladder Cancer.Front Genet. 2020 Jun 23;11:607. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00607. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32655621 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dunn GP, Old LJ, Schreiber RD. The three Es of cancer immunoediting. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:329–360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials