Ketoacidosis at first presentation of type 1 diabetes mellitus among children: a study from Kuwait
- PMID: 27328757
- PMCID: PMC4916451
- DOI: 10.1038/srep27519
Ketoacidosis at first presentation of type 1 diabetes mellitus among children: a study from Kuwait
Abstract
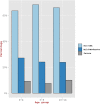
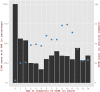
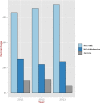
We examined the frequency and severity of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) in 679 children and adolescents (0-14 years) at diagnosis of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM) in Kuwait. Between 1(st) January 2011 and 31(st) December 2013, all newly diagnosed children with diabetes were registered prospectively in a population-based electronic register. DKA was diagnosed using standard criteria based on the levels of venous pH and serum bicarbonate. At the time of diagnosis, mild/moderate DKA was present in 24.8% of the children, while severe DKA was present in 8.8%. Incidence of ketoacidosis was significantly higher in young children less than 2 (60.7% vs 32.4% p = <0.005) compared to children 2-14 years old, and a higher proportion presented with severe DKA (21.4% vs 8.3% p = <0.05). No association was seen with gender. Significant differences were found in the incidence of DKA between Kuwaiti and non-Kuwaiti children (31.1% vs 39.8%; p < 0.05). Family history of diabetes had a protective effect on the occurrence of DKA (OR = 0.44; 95% CI = 0.27-0.71). Incidence of DKA in children at presentation of T1DM remains high at 33.6%. Prevention campaigns are needed to increase public awareness among health care providers, parents and school teachers in Kuwait.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ketoacidosis at presentation of type 1 diabetes in children in Kuwait: frequency and clinical characteristics.Pediatr Diabetes. 2010 Aug;11(5):351-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2009.00600.x. Pediatr Diabetes. 2010. PMID: 19821943
-
Identifying targets to reduce the incidence of diabetic ketoacidosis at diagnosis of type 1 diabetes in the UK.Arch Dis Child. 2014 May;99(5):438-42. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2013-304818. Epub 2014 Jan 6. Arch Dis Child. 2014. PMID: 24395643
-
First report on the nationwide incidence of type 1 diabetes and ketoacidosis at onset in children in Serbia: a multicenter study.Eur J Pediatr. 2018 Aug;177(8):1155-1162. doi: 10.1007/s00431-018-3172-4. Epub 2018 May 17. Eur J Pediatr. 2018. PMID: 29774417
-
Incidence of diabetic ketoacidosis during COVID-19 pandemic: a meta-analysis of 124,597 children with diabetes.Pediatr Res. 2023 Apr;93(5):1149-1160. doi: 10.1038/s41390-022-02241-2. Epub 2022 Aug 11. Pediatr Res. 2023. PMID: 35953513 Free PMC article.
-
Ketoacidosis at onset of type 1 diabetes mellitus in pediatric age in Spain and review of the literature.Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2012 Mar;9(3):669-71. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22523835 Review.
Cited by
-
Frequency, Clinical Characteristics and Predictors of Ketoacidosis at Diagnosis of Type One Diabetes Mellitus in Children and Adolescents from Jordan.J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2023 Feb 27;15(1):46-54. doi: 10.4274/jcrpe.galenos.2022.2022-5-8. Epub 2022 Oct 20. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 36264035 Free PMC article.
-
Blood Urea Nitrogen to Serum Albumin Ratio as A New Prognostic Indicator in Critically Ill Patients with Diabetic Ketoacidosis: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2024 May;132(5):249-259. doi: 10.1055/a-2274-0389. Epub 2024 Feb 22. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38387890 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiological trends in the presentation of diabetic ketoacidosis in children newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes from 2011 to 2017 in Kuwait.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 9;13:908458. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.908458. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36568099 Free PMC article.
-
[Diabetic ketoacidosis in children: epidemiological and prognostic aspects].Pan Afr Med J. 2018 Nov 9;31:167. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2018.31.167.14415. eCollection 2018. Pan Afr Med J. 2018. PMID: 31086620 Free PMC article. French.
-
Early Onset of Type 1 Diabetes in Kuwait: Distinct Clinical, Metabolic, and Immunological Characteristics.Med Princ Pract. 2024;33(6):555-561. doi: 10.1159/000540705. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Med Princ Pract. 2024. PMID: 39097968 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Szypowska A. & Skórka A. The risk factors of ketoacidosis in children with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus. Pediatr. Diabetes 12, 302–306 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Rosenbloom A. L. Intracerebral crises during treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetes Care 13, 22–33 (1990). - PubMed
-
- Lokulo-Sodipe K., Moon R. J., Edge J. A. & Davies J. H. Identifying targets to reduce the incidence of diabetic ketoacidosis at diagnosis of type 1 diabetes in the UK. Arch. Dis. Child. 99, 438–442 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

