Activins and Inhibins: Roles in Development, Physiology, and Disease
- PMID: 27328872
- PMCID: PMC4930927
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a021881
Activins and Inhibins: Roles in Development, Physiology, and Disease
Abstract
Since their original discovery as regulators of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) secretion and erythropoiesis, the TGF-β family members activin and inhibin have been shown to participate in a variety of biological processes, from the earliest stages of embryonic development to highly specialized functions in terminally differentiated cells and tissues. Herein, we present the history, structures, signaling mechanisms, regulation, and biological processes in which activins and inhibins participate, including several recently discovered biological activities and functional antagonists. The potential therapeutic relevance of these advances is also discussed.
Copyright © 2016 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures
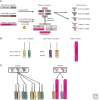
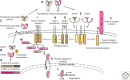
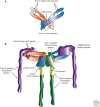

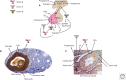

References
-
- Acharyya S, Guttridge DC. 2007. Cancer cachexia signaling pathways continue to emerge yet much still points to the proteasome. Clin Cancer Res 13: 1356–1361. - PubMed
-
- Ageta H, Ikegami S, Miura M, Masuda M, Migishima R, Hino T, Takashima N, Murayama A, Sugino H, Setou M, et al. 2010. Activin plays a key role in the maintenance of long-term memory and late-LTP. Learn Mem 17: 176–185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
