The THO/TREX Complex Active in miRNA Biogenesis Negatively Regulates Root-Associated Acid Phosphatase Activity Induced by Phosphate Starvation
- PMID: 27329222
- PMCID: PMC4972289
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.16.00680
The THO/TREX Complex Active in miRNA Biogenesis Negatively Regulates Root-Associated Acid Phosphatase Activity Induced by Phosphate Starvation
Abstract
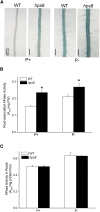
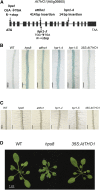
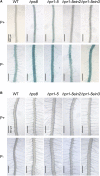
Induction and secretion of acid phosphatases (APases) is an adaptive response that plants use to cope with P (Pi) deficiency in their environment. The molecular mechanism that regulates this response, however, is poorly understood. In this work, we identified an Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) mutant, hps8, which exhibits enhanced APase activity on its root surface (also called root-associated APase activity). Our molecular and genetic analyses indicate that this altered Pi response results from a mutation in the AtTHO1 gene that encodes a subunit of the THO/TREX protein complex. The mutation in another subunit of this complex, AtTHO3, also enhances root-associated APase activity under Pi starvation. In Arabidopsis, the THO/TREX complex functions in mRNA export and miRNA biogenesis. When treated with Ag(+), an inhibitor of ethylene perception, the enhanced root-associated APase activity in hps8 is largely reversed. hpr1-5 is another mutant allele of AtTHO1 and shows similar phenotypes as hps8 ein2 is completely insensitive to ethylene. In the hpr1-5ein2 double mutant, the enhanced root-associated APase activity is also greatly suppressed. These results indicate that the THO/TREX complex in Arabidopsis negatively regulates root-associated APase activity induced by Pi starvation by inhibiting ethylene signaling. In addition, we found that the miRNA399-PHO2 pathway is also involved in the regulation of root-associated APase activity induced by Pi starvation. These results provide insight into the molecular mechanism underlying the adaptive response of plants to Pi starvation.
© 2016 American Society of Plant Biologists. All Rights Reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A major root-associated acid phosphatase in Arabidopsis, AtPAP10, is regulated by both local and systemic signals under phosphate starvation.J Exp Bot. 2014 Dec;65(22):6577-88. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru377. Epub 2014 Sep 22. J Exp Bot. 2014. PMID: 25246445 Free PMC article.
-
The Arabidopsis gene hypersensitive to phosphate starvation 3 encodes ethylene overproduction 1.Plant Cell Physiol. 2012 Jun;53(6):1093-105. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcs072. Epub 2012 May 22. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22623414
-
The Arabidopsis purple acid phosphatase AtPAP10 is predominantly associated with the root surface and plays an important role in plant tolerance to phosphate limitation.Plant Physiol. 2011 Nov;157(3):1283-99. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.183723. Epub 2011 Sep 22. Plant Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21941000 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptation to Phosphate Scarcity: Tips from Arabidopsis Roots.Trends Plant Sci. 2018 Aug;23(8):721-730. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2018.04.006. Epub 2018 May 12. Trends Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 29764728 Review.
-
Functions and regulation of phosphate starvation-induced secreted acid phosphatases in higher plants.Plant Sci. 2018 Jun;271:108-116. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.03.013. Epub 2018 Mar 14. Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 29650148 Review.
Cited by
-
Ubiquitination and Ubiquitin-Like Modifications as Mediators of Alternative Pre-mRNA Splicing in Arabidopsis thaliana.Front Plant Sci. 2022 May 12;13:869870. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.869870. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35646014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-throughput sequencing analysis revealed the regulation patterns of small RNAs on the development of A. comosus var. bracteatus leaves.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 31;8(1):1947. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20261-z. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29386560 Free PMC article.
-
The THO/TREX Complex Component RAE2/TEX1 Is Involved in the Regulation of Aluminum Resistance and Low Phosphate Response in Arabidopsis.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Jul 12;12:698443. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.698443. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34322147 Free PMC article.
-
The THO/TREX Complex Active in Alternative Splicing Mediates Plant Responses to Salicylic Acid and Jasmonic Acid.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 11;22(22):12197. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212197. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830079 Free PMC article.
-
The transcription and export complex THO/TREX contributes to transcription termination in plants.PLoS Genet. 2020 Apr 13;16(4):e1008732. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008732. eCollection 2020 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 32282821 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16: 735–743 - PubMed
-
- del Pozo JC, Allona I, Rubio V, Leyva A, de la Peña A, Aragoncillo C, Paz-Ares J (1999) A type 5 acid phosphatase gene from Arabidopsis thaliana is induced by phosphate starvation and by some other types of phosphate mobilising/oxidative stress conditions. Plant J 19: 579–589 - PubMed
-
- Del Vecchio HA, Ying S, Park J, Knowles VL, Kanno S, Tanoi K, She YM, Plaxton WC (2014) The cell wall-targeted purple acid phosphatase AtPAP25 is critical for acclimation of Arabidopsis thaliana to nutritional phosphorus deprivation. Plant J 80: 569–581 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

