Structural basis of suppression of host translation termination by Moloney Murine Leukemia Virus
- PMID: 27329342
- PMCID: PMC4917968
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms12070
Structural basis of suppression of host translation termination by Moloney Murine Leukemia Virus
Abstract
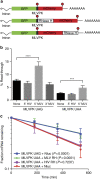
Retroviral reverse transcriptase (RT) of Moloney murine leukemia virus (MoMLV) is expressed in the form of a large Gag-Pol precursor protein by suppression of translational termination in which the maximal efficiency of stop codon read-through depends on the interaction between MoMLV RT and peptidyl release factor 1 (eRF1). Here, we report the crystal structure of MoMLV RT in complex with eRF1. The MoMLV RT interacts with the C-terminal domain of eRF1 via its RNase H domain to sterically occlude the binding of peptidyl release factor 3 (eRF3) to eRF1. Promotion of read-through by MoMLV RNase H prevents nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) of mRNAs. Comparison of our structure with that of HIV RT explains why HIV RT cannot interact with eRF1. Our results provide a mechanistic view of how MoMLV manipulates the host translation termination machinery for the synthesis of its own proteins.
Figures
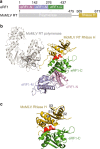




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

