Role of microRNA-4516 involved autophagy associated with exposure to fine particulate matter
- PMID: 27329587
- PMCID: PMC5216729
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.9978
Role of microRNA-4516 involved autophagy associated with exposure to fine particulate matter
Abstract
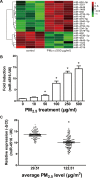
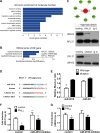
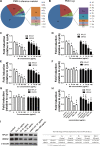
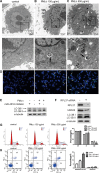
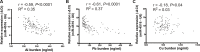
Metals are vital toxic components of fine particulate matter (PM2.5). Cellular responses to exposure to PM2.5 or PM metal components remain unknown. Post-transcriptional profiling and subsequent cell- and individual-based assays implied that the metal ion-binding miR-4516/RPL37/autophagy pathway could play a critical role in cellular responses to PM2.5 and PM metal stresses. miR-4516 was up-regulated in A549 cells exposed to PM2.5 and in the serum of individuals living in a city with moderate air pollution. The expression levels of the miR-4516 target genes, namely, RPL37 and UBA52, were involved in ribosome function and inhibited by exposure to PM2.5 and PM metal components. Autophagy in A549 cells was induced by PM2.5 exposure as a response to decreased RPL37 expression. Moreover, enhanced miR-4516 expression was positively correlated with the augmentation of the internal burden of aluminum and lead in individuals living in a city with moderate air pollution. Hereby, the miR-4516/RPL37/autophagy pathway may represent a novel mechanism that mediates responses to PM metal components.
Keywords: PM2.5; autophagy; metal; microRNA; ribosome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Beelen R, Raaschou-Nielsen O, Stafoggia M, Andersen ZJ, Weinmayr G, Hoffmann B, Wolf K, Samoli E, Fischer P, Nieuwenhuijsen M, Vineis P, Xun WW, Katsouyanni K, et al. Effects of long-term exposure to air pollution on natural-cause mortality: an analysis of 22 European cohorts within the multicentre ESCAPE project. Lancet. 2014;383:785–795. - PubMed
-
- Raaschou-Nielsen O, Andersen ZJ, Beelen R, Samoli E, Stafoggia M, Weinmayr G, Hoffmann B, Fischer P, Nieuwenhuijsen MJ, Brunekreef B, Xun WW, Katsouyanni K, Dimakopoulou K, et al. Air pollution and lung cancer incidence in 17 European cohorts: prospective analyses from the European Study of Cohorts for Air Pollution Effects (ESCAPE) Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:813–822. - PubMed
-
- Loomis D, Grosse Y, Lauby-Secretan B, El Ghissassi F, Bouvard V, Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Guha N, Baan R, Mattock H, Straif K, International Agency for Research on Cancer Monograph Working Group I The carcinogenicity of outdoor air pollution. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:1262–1263. - PubMed
-
- Dergham M, Lepers C, Verdin A, Cazier F, Billet S, Courcot D, Shirali P, Garcon G. Temporal-spatial variations of the physicochemical characteristics of air pollution Particulate Matter (PM2.5-0.3) and toxicological effects in human bronchial epithelial cells (BEAS-2B) Environ Res. 2015;137:256–267. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

