Genome-wide association study of 40,000 individuals identifies two novel loci associated with bipolar disorder
- PMID: 27329760
- PMCID: PMC5179929
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddw181
Genome-wide association study of 40,000 individuals identifies two novel loci associated with bipolar disorder
Abstract
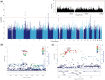
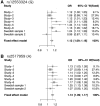
Bipolar disorder (BD) is a genetically complex mental illness characterized by severe oscillations of mood and behaviour. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified several risk loci that together account for a small portion of the heritability. To identify additional risk loci, we performed a two-stage meta-analysis of >9 million genetic variants in 9,784 bipolar disorder patients and 30,471 controls, the largest GWAS of BD to date. In this study, to increase power we used ∼2,000 lithium-treated cases with a long-term diagnosis of BD from the Consortium on Lithium Genetics, excess controls, and analytic methods optimized for markers on the X-chromosome. In addition to four known loci, results revealed genome-wide significant associations at two novel loci: an intergenic region on 9p21.3 (rs12553324, P = 5.87 × 10 - 9; odds ratio (OR) = 1.12) and markers within ERBB2 (rs2517959, P = 4.53 × 10 - 9; OR = 1.13). No significant X-chromosome associations were detected and X-linked markers explained very little BD heritability. The results add to a growing list of common autosomal variants involved in BD and illustrate the power of comparing well-characterized cases to an excess of controls in GWAS.
Published by Oxford University Press 2016. This work is written by US Government employees and is in the public domain in the United States.
Figures
References
-
- McGuffin P., Rijsdijk F., Andrew M., Sham P., Katz R., Cardno A. (2003) The heritability of bipolar affective disorder and the genetic relationship to unipolar depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry, 60, 497–502. - PubMed
-
- Edvardsen J., Torgersen S., Roysamb E., Lygren S., Skre I., Onstad S., Oien P.A. (2008) Heritability of bipolar spectrum disorders. Unity or heterogeneity? J. Affect. Disord., 106, 229–240. - PubMed
-
- Baum A.E., Akula N., Cabanero M., Cardona I., Corona W., Klemens B., Schulze T.G., Cichon S., Rietschel M., Nothen M.M., et al. (2008) A genome-wide association study implicates diacylglycerol kinase eta (DGKH) and several other genes in the etiology of bipolar disorder. Mol. Psychiatry, 13, 197–207. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 MH059556/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA006227/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059535/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090936/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001108/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059548/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059534/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059533/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090951/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 MH101822/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060068/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101782/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059567/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059545/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101810/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101819/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA089392/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 MH002810/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA033684/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K02 DA021237/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101820/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101825/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090948/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090941/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001C/RC/CCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059553/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH090937/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201000029C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001E/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101814/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

