Structure of the Achilles tendon at the insertion on the calcaneal tuberosity
- PMID: 27330029
- PMCID: PMC5055086
- DOI: 10.1111/joa.12514
Structure of the Achilles tendon at the insertion on the calcaneal tuberosity
Abstract
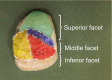
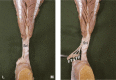
Findings on the twisting structure and insertional location of the AT on the calcaneal tuberosity are inconsistent. Therefore, to obtain a better understanding of the mechanisms underlying insertional Achilles tendinopathy, clarification of the anatomy of the twisting structure and location of the AT insertion onto the calcaneal tuberosity is important. The purpose of this study was to reveal the twisted structure of the AT and the location of its insertion onto the calcaneal tuberosity using Japanese cadavers. The study was conducted using 132 legs from 74 cadavers (mean age at death, 78.3 ± 11.1 years; 87 sides from men, 45 from women). Only soleus (Sol) attached to the deep layer of the calcaneal tuberosity was classified as least twist (Type I), both the lateral head of the gastrocnemius (LG) and Sol attached to the deep layer of the calcaneal tuberosity were classified as moderate twist (Type II), and only LG attached to the deep layer of the calcaneal tuberosity was classified as extreme twist (Type III). The Achilles tendon insertion onto the calcaneal tuberosity was classified as a superior, middle or inferior facet. Twist structure was Type I (least) in 31 legs (24%), Type II (moderate) in 87 legs (67%), and Type III (extreme) in 12 legs (9%). A comparison between males and females revealed that among men, 20 legs (24%) were Type I, 57 legs (67%) Type II, and eight legs (9%) Type III. Among women, 11 legs (24%) were Type I, 30 legs (67%) Type II, and four legs (9%) Type III. No significant differences were apparent between sexes. The fascicles of the Achilles tendon attach mainly in the middle facet. Anterior fibers of the Achilles tendon, where insertional Achilles tendinopathy is most likely, are Sol in Type I, LG and Sol in Type II, and LG only in Type III. This suggests the possibility that a different strain is produced in the anterior fibers of the Achilles tendon (calcaneal side) where insertional Achilles tendinopathy is most likely to occur in each type. We look forward to elucidating the mechanisms generating insertional Achilles tendinopathy in future biomedical studies based on the present results.
Keywords: Achilles tendon disorders; Japanese cadavers; insertional Achilles tendinopathy; insertional site.
© 2016 Anatomical Society.
Figures

References
-
- Ballal MS, Walker CR, Molloy AP (2014) The anatomical footprint of the Achilles tendon: a cadaveric study. Bone Joint J 96‐b, 1344–1348. - PubMed
-
- Bojsen‐Moller J, Magnusson SP (2015) Heterogeneous loading of the human Achilles tendon in vivo. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 43, 190–197. - PubMed
-
- Bojsen‐Moller J, Hansen P, Aagaard P, et al. (2004) Differential displacement of the human soleus and medial gastrocnemius aponeuroses during isometric plantar flexor contractions in vivo. J Appl Physiol (1985) 97, 1908–1914. - PubMed
-
- Carr AJ, Norris SH (1989) The blood supply of the calcaneal tendon. J Bone Joint Surg Br 71, 100–101. - PubMed
-
- Clain MR, Baxter DE (1992) Achilles tendinitis. Foot Ankle 13, 482–487. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

