Structural Elements in the Gαs and Gαq C Termini That Mediate Selective G Protein-coupled Receptor (GPCR) Signaling
- PMID: 27330078
- PMCID: PMC5016181
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.735720
Structural Elements in the Gαs and Gαq C Termini That Mediate Selective G Protein-coupled Receptor (GPCR) Signaling
Abstract
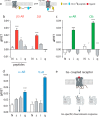
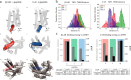
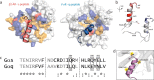
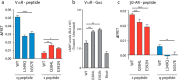
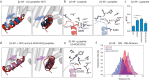
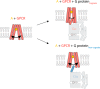
Although the importance of the C terminus of the α subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein in G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR)-G protein pairing is well established, the structural basis of selective interactions remains unknown. Here, we combine live cell FRET-based measurements and molecular dynamics simulations of the interaction between the GPCR and a peptide derived from the C terminus of the Gα subunit (Gα peptide) to dissect the molecular mechanisms of G protein selectivity. We observe a direct link between Gα peptide binding and stabilization of the GPCR conformational ensemble. We find that cognate and non-cognate Gα peptides show deep and shallow binding, respectively, and in distinct orientations within the GPCR. Binding of the cognate Gα peptide stabilizes the agonist-bound GPCR conformational ensemble resulting in favorable binding energy and lower flexibility of the agonist-GPCR pair. We identify three hot spot residues (Gαs/Gαq-Gln-384/Leu-349, Gln-390/Glu-355, and Glu-392/Asn-357) that contribute to selective interactions between the β2-adrenergic receptor (β2-AR)-Gαs and V1A receptor (V1AR)-Gαq The Gαs and Gαq peptides adopt different orientations in β2-AR and V1AR, respectively. The β2-AR/Gαs peptide interface is dominated by electrostatic interactions, whereas the V1AR/Gαq peptide interactions are predominantly hydrophobic. Interestingly, our study reveals a role for both favorable and unfavorable interactions in G protein selection. Residue Glu-355 in Gαq prevents this peptide from interacting strongly with β2-AR. Mutagenesis to the Gαs counterpart (E355Q) imparts a cognate-like interaction. Overall, our study highlights the synergy in molecular dynamics and FRET-based approaches to dissect the structural basis of selective G protein interactions.
Keywords: G protein; G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR); Receptor Conformation; cell signaling; fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET); molecular dynamics.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Kobilka B., and Schertler G. F. (2008) New G-protein-coupled receptor crystal structures: insights and limitations. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 29, 79–83 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

