Adaptable history biases in human perceptual decisions
- PMID: 27330086
- PMCID: PMC4922170
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1518786113
Adaptable history biases in human perceptual decisions
Abstract
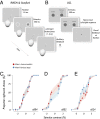
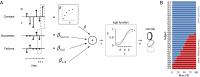
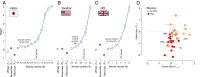
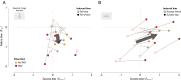
When making choices under conditions of perceptual uncertainty, past experience can play a vital role. However, it can also lead to biases that worsen decisions. Consistent with previous observations, we found that human choices are influenced by the success or failure of past choices even in a standard two-alternative detection task, where choice history is irrelevant. The typical bias was one that made the subject switch choices after a failure. These choice history biases led to poorer performance and were similar for observers in different countries. They were well captured by a simple logistic regression model that had been previously applied to describe psychophysical performance in mice. Such irrational biases seem at odds with the principles of reinforcement learning, which would predict exquisite adaptability to choice history. We therefore asked whether subjects could adapt their irrational biases following changes in trial order statistics. Adaptability was strong in the direction that confirmed a subject's default biases, but weaker in the opposite direction, so that existing biases could not be eradicated. We conclude that humans can adapt choice history biases, but cannot easily overcome existing biases even if irrational in the current context: adaptation is more sensitive to confirmatory than contradictory statistics.
Keywords: bias adaptation; choice bias; choice history; computational modeling; decision making.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Nowak M, Sigmund K. A strategy of win-stay, lose-shift that outperforms tit-for-tat in the Prisoner’s Dilemma game. Nature. 1993;364(6432):56–58. - PubMed
-
- Sutton SR, Barto AG. Reinforcement Learning. MIT Press; Cambridge, MA: 1998.
-
- Daw ND, Doya K. The computational neurobiology of learning and reward. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2006;16(2):199–204. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

