Structures of the orthosomycin antibiotics avilamycin and evernimicin in complex with the bacterial 70S ribosome
- PMID: 27330110
- PMCID: PMC4941455
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1604790113
Structures of the orthosomycin antibiotics avilamycin and evernimicin in complex with the bacterial 70S ribosome
Abstract
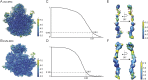
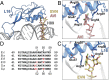
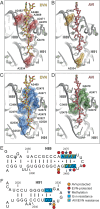
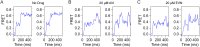
The ribosome is one of the major targets for therapeutic antibiotics; however, the rise in multidrug resistance is a growing threat to the utility of our current arsenal. The orthosomycin antibiotics evernimicin (EVN) and avilamycin (AVI) target the ribosome and do not display cross-resistance with any other classes of antibiotics, suggesting that they bind to a unique site on the ribosome and may therefore represent an avenue for development of new antimicrobial agents. Here we present cryo-EM structures of EVN and AVI in complex with the Escherichia coli ribosome at 3.6- to 3.9-Å resolution. The structures reveal that EVN and AVI bind to a single site on the large subunit that is distinct from other known antibiotic binding sites on the ribosome. Both antibiotics adopt an extended conformation spanning the minor grooves of helices 89 and 91 of the 23S rRNA and interacting with arginine residues of ribosomal protein L16. This binding site overlaps with the elbow region of A-site bound tRNA. Consistent with this finding, single-molecule FRET (smFRET) experiments show that both antibiotics interfere with late steps in the accommodation process, wherein aminoacyl-tRNA enters the peptidyltransferase center of the large ribosomal subunit. These data provide a structural and mechanistic rationale for how these antibiotics inhibit the elongation phase of protein synthesis.
Keywords: Ziracin; antimicrobial; cryo-EM; everninomicin; rRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Wilson DN. Ribosome-targeting antibiotics and mechanisms of bacterial resistance. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2014;12(1):35–48. - PubMed
-
- Wilson DN. The A-Z of bacterial translation inhibitors. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2009;44(6):393–433. - PubMed
-
- Wright D. The orthosomycins, a new family of antibiotics. Tetrahedron. 1979;35(10):1209–1327.
-
- Buzzetti F, et al. [Avilamycin] Experientia. 1968;24(4):320–323. - PubMed
-
- Wagman GH, Luedemann GM, Weinstein MJ. Fermentation and isolation of everninomicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1964;10:33–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

