Molecular dynamics simulations on the effect of size and shape on the interactions between negative Au18(SR)14, Au102(SR)44 and Au144(SR)60 nanoparticles in physiological saline
- PMID: 27330249
- PMCID: PMC4911198
- DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2016.05.038
Molecular dynamics simulations on the effect of size and shape on the interactions between negative Au18(SR)14, Au102(SR)44 and Au144(SR)60 nanoparticles in physiological saline
Abstract
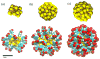
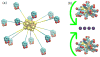
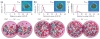
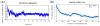
Molecular dynamics simulations employing all-atom force fields have become a reliable way to study binding interactions quantitatively for a wide range of systems. In this work, we employ two recently developed methods for the calculation of dissociation constants KD between gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) of different sizes in a near-physiological environment through the potential of mean force (PMF) formalism: the method of geometrical restraints developed by Woo et al. and formalized by Gumbart et al. and the method of hybrid Steered Molecular Dynamics (hSMD). Obtaining identical results (within the margin of error) from both approaches on the negatively charged Au18(SR)14 NP, functionalized by the negatively charged 4-mercapto-benzoate (pMBA) ligand, we draw parallels between their energetic and entropic interactions. By applying the hSMD method on Au102(SR)44 and Au144(SR)60, both of them near-spherical in shape and functionalized by pMBA, we study the effects of size and shape on the binding interactions. Au18 binds weakly with KD = 13mM as a result of two opposing effects: its large surface curvature hindering the formation of salt bridges, and its large ligand density on preferential orientations favoring their formation. On the other hand, Au102 binds more strongly with KD = 30μM and Au144 binds the strongest with KD = 3.2nM.
Keywords: Aggregation; Gold Nanoparticles; Molecular Dynamics.
Figures
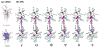

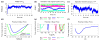
References
-
- Jabes BS, Yadav HOS, Kumar SK, Chakravarty C. Fluctuation-driven anisotropy in effective pair interactions between nanoparticles: Thiolated gold nanoparticles in ethane. J Chem Phys. 2014;141(15):154904. doi:doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4897541. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sun L, Yang X, Wu B, Tang L. Molecular simulation of interaction between passivated gold nanoparticles in supercritical co2. J Chem Phys. 2011;135(20):204703. doi:doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.3661982. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Patel N, Egorov SA. Interactions between sterically stabilized nanoparticles in supercritical fluids: A simulation study. J Chem Phys. 2007;126(5):054706. doi:doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.2434155. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Heikkil E, Martinez-Seara H, Gurtovenko AA, Javanainen M, Hkkinen H, Vattulainen I, Akola J. Cationic au nanoparticle binding with plasma membrane-like lipid bilayers: Potential mechanism for spontaneous permeation to cells revealed by atomistic simulations. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C. 2014;118(20):11131–11141. doi: 10.1021/jp5024026. arXiv: http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jp5024026. - DOI - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
