Isolation and characterization of cyclo-(tryptophanyl-prolyl) and chloramphenicol from Streptomyces sp. SUK 25 with antimethicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus activity
- PMID: 27330275
- PMCID: PMC4896468
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S101212
Isolation and characterization of cyclo-(tryptophanyl-prolyl) and chloramphenicol from Streptomyces sp. SUK 25 with antimethicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus activity
Abstract
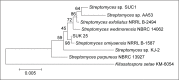
Background: Zingiber spectabile, commonly known as Beehive Ginger, is used as an ethnobotanical plant in many countries as an appetizer or to treat stomachache, toothache, muscle sprain, and as a cure for swelling, sores and cuts. This is the first report of isolation of Streptomyces strain from the root of this plant. Strain Universiti Kebangsaan 25 (SUK 25) has a very high activity to produce secondary metabolites against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), which is associated with high morbidity and mortality rates due to acquired multidrug resistance genes and causes medication failure in some clinical cases worldwide. Phylogenetic analysis based on the 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequence exhibited that the most closely related strain was Streptomyces omiyaensis NBRC 13449T (99.0% similarity).
Aim: This study was conducted to carry out the extraction, identification, and biological evaluation of active metabolites isolated from SUK 25 against three MRSA strains, namely, MRSA ATCC 43300, MRSA ATCC 33591, and MRSA ATCC 49476.
Materials and methods: The production of secondary metabolites by this strain was optimized through Thronton's media. Isolation, purification, and identification of the bioactive compounds were carried out using reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography, high-resolution mass spectrometry, Fourier transform infrared, and one-dimensional and two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance.
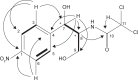
Results: During screening procedure, SUK 25 exhibited good antimicrobial potential against several strains of MRSA. The best biological activity was shown from fraction number VII and its subfractions F2 and F3 with minimum inhibitory concentration values at 16 µg/mL and 8 µg/mL, respectively. These two subfractions were identified as diketopiperazine cyclo-(tryptophanyl-prolyl) and chloramphenicol.
Conclusion: On the basis of obtained results, SUK 25 isolated from Z. spectabile can be regarded as a new valuable source to produce secondary metabolites against bacteria, especially MRSA.
Keywords: HR-MS; MRSA; NMR; SUK 25; Zingiber spectabile; chloramphenicol; cyclo-(tryptophanyl-prolyl).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Isolation, Purification, and Characterization of Five Active Diketopiperazine Derivatives from Endophytic Streptomyces SUK 25 with Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Activities.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017 Jul 28;27(7):1249-1256. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1608.08032. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28535606
-
Profiling of gene expression in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in response to cyclo-(L-Val-L-Pro) and chloramphenicol isolated from Streptomyces sp., SUK 25 reveals gene downregulation in multiple biological targets.Arch Microbiol. 2020 Oct;202(8):2083-2092. doi: 10.1007/s00203-020-01896-x. Epub 2020 Jun 3. Arch Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32494868
-
Purification and characterization of actinomycins from Streptomyces strain M7 active against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin resistant Enterococcus.BMC Microbiol. 2019 Feb 19;19(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12866-019-1405-y. BMC Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30782119 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial potential and taxonomic investigation of piezotolerant Streptomyces sp. NIOT-Ch-40 isolated from deep-sea sediment.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017 Feb;33(2):27. doi: 10.1007/s11274-016-2193-2. Epub 2017 Jan 2. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28044276
-
Streptomyces as a Prominent Resource of Future Anti-MRSA Drugs.Front Microbiol. 2018 Sep 24;9:2221. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02221. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30319563 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biodiversity of Secondary Metabolites Compounds Isolated from Phylum Actinobacteria and Its Therapeutic Applications.Molecules. 2021 Jul 26;26(15):4504. doi: 10.3390/molecules26154504. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34361657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibacterial Activity of Endophytic Actinomycetes Isolated from the Medicinal Plant Vochysia divergens (Pantanal, Brazil).Front Microbiol. 2017 Sep 6;8:1642. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01642. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28932210 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Pharmaceutically Active Compounds Productivity from Streptomyces SUK 25: Optimization, Characterization, Mechanism and Techno-Economic Analysis.Molecules. 2021 Apr 25;26(9):2510. doi: 10.3390/molecules26092510. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33923072 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Action Mechanisms of Natural Compounds Isolated from Endophytic Microorganisms.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Mar 18;13(3):271. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13030271. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38534706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial potentials of natural products against multidrug resistance pathogens: a comprehensive review.RSC Adv. 2022 Oct 13;12(45):29078-29102. doi: 10.1039/d2ra04884a. eCollection 2022 Oct 11. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 36320761 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tayung K, Sarkar M, Baruah P. Endophytic fungi occurring in Ipomoea carnea tissues and their antimicrobial potentials. Braz Arch Biol Technol. 2012;55(5):653–660.
-
- Shukla Y, Singh M. Cancer preventive properties of ginger: a brief review. Food Chem Toxicol. 2007;45(5):683–690. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

