Indigofera oblongifolia mitigates lead-acetate-induced kidney damage and apoptosis in a rat model
- PMID: 27330278
- PMCID: PMC4898036
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S105511
Indigofera oblongifolia mitigates lead-acetate-induced kidney damage and apoptosis in a rat model
Abstract
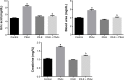
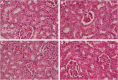
This study was conducted to appraise the protective effect of Indigofera oblongifolia leaf extract on lead acetate (PbAc)-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. PbAc was intraperitoneally injected at a dose of 20 mg/kg body weight for 5 days, either alone or together with the methanol extract of I. oblongifolia (100 mg/kg). Kidney lead (Pb) concentration; oxidative stress markers including lipid peroxidation, nitrite/nitrate, and glutathione (GSH); and antioxidant enzyme activities, namely superoxide dismutase, catalase, GSH peroxidase, and GSH reductase were all determined. The PbAc injection elicited a marked elevation in Pb concentration, lipid peroxidation, and nitrite/nitrate, with a concomitant depletion in GSH content compared with the control and a remarkable decrease in antioxidant enzymes. Oxidant/antioxidant imbalance, Pb accumulation, and histological changes in the kidneys were successfully prevented by the pre-administration of I. oblongifolia extract. In addition, the elevated expression of proapoptotic protein, Bax, in the kidneys of the PbAc-injected rats was reduced as a result of I. oblongifolia pre-administration, while the hitherto reduced expression of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 was elevated. Based on the current findings, it can be concluded that I. oblongifolia successfully minimizes the deleterious effects in kidney function and histological coherence associated with nephrotoxicity by strengthening the antioxidant defense system, suppressing oxidative stress, and mitigating apoptosis.
Keywords: Indigofera oblongifolia; apoptosis; kidney; lead acetate; oxidative stress.
Figures
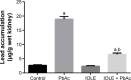



References
-
- Jia Q, Ha X, Yang Z, Hui L, Yang X. Oxidative stress: a possible mechanism for lead-induced apoptosis and nephrotoxicity. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2012;22(9):705–710. - PubMed
-
- Jabeen R, Tahir M, Waqas S. Teratogenic effects of lead acetate on kidney. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2010;22(1):76–79. - PubMed
-
- Abdel Moneim AE, Dkhil MA, Al-Quraishy S. The protective effect of flaxseed oil on lead acetate-induced renal toxicity in rats. J Hazard Mater. 2011;194:250–255. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

