Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of ipragliflozin in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and inadequate glycemic control with metformin: Results of a phase 3 randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, multicenter trial
- PMID: 27330723
- PMCID: PMC4847891
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.12422
Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of ipragliflozin in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and inadequate glycemic control with metformin: Results of a phase 3 randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, multicenter trial
Abstract
Aims/introduction: To determine the efficacy and safety of ipragliflozin in combination with metformin in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Materials and methods: This phase 3, multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel-group study was carried out at 18 sites in Korea and 12 sites in Taiwan. After an 8-week washout period for patients using drugs other than metformin and a 2-week run-in period, patients were randomized to either 50 mg ipragliflozin or a placebo for 24 weeks while continuing metformin. Efficacy outcomes included the changes in hemoglobin A1c, fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and bodyweight from baseline to the end of treatment (with last observation carried forward). Safety outcomes included treatment-emergent adverse events.
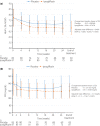
Results: Between November 2011 and January 2013, 171 patients were randomized to and administered ipragliflozin (n = 87) or a placebo (n = 83). The mean changes (standard deviation) in hemoglobin A1c were -0.94% (0.75%) and -0.47% (0.81%) in the ipragliflozin and placebo groups, respectively (between-group difference -0.46%, P < 0.001). The changes in fasting plasma glucose and bodyweight were also significantly greater in the ipragliflozin group, with between-group differences of -14.1 mg/dL and -1.24 kg, respectively (both P < 0.001). The most common treatment-emergent adverse events (ipragliflozin vs placebo) were upper respiratory tract infection (9.2% vs 12.0%) and urinary tract infection (6.9% vs 2.4%).
Conclusions: These results show that ipragliflozin is effective and well tolerated when used in combination with metformin in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Keywords: Asia; Ipragliflozin; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Figures
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation . IDF Diabetes Atlas, 6th edn Brussels: International Diabetes Federation, 2013.
-
- Chan JC, Malik V, Jia W, et al Diabetes in Asia: epidemiology, risk factors, and pathophysiology. JAMA 2009; 301: 2129–2140. - PubMed
-
- International Diabetes Federation Global Guidelines Task Force . Global Guideline for Type 2 Diabetes. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation, 2011.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical