Enrofloxacin enhances the effects of chemotherapy in canine osteosarcoma cells with mutant and wild-type p53
- PMID: 27333821
- PMCID: PMC5182190
- DOI: 10.1111/vco.12250
Enrofloxacin enhances the effects of chemotherapy in canine osteosarcoma cells with mutant and wild-type p53
Abstract
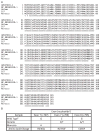
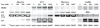
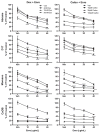
Adjuvant chemotherapy improves survival time in dogs receiving adequate local control for appendicular osteosarcoma, but most dogs ultimately succumb to metastatic disease. The fluoroquinolone antibiotic enrofloxacin has been shown to inhibit survival and proliferation of canine osteosarcoma cells in vitro. Others have reported that fluoroquinolones may modulate cellular responses to DNA damaging agents and that these effects may be differentially mediated by p53 activity. We therefore determined p53 status and activity in three canine osteosarcoma cell lines and examined the effects of enrofloxacin when used alone or in combination with doxorubicin or carboplatin chemotherapy. Moresco and Abrams canine osteosarcoma cell lines contained mutations in p53, while no mutations were identified in the D17 cells or in a normal canine osteoblast cell line. The addition of enrofloxacin to either doxorubicin or carboplatin resulted in further reductions in osteosarcoma cell viability; this effect was apparent regardless of p53 mutational status or downstream activity.
Keywords: chemotherapy; comparative oncology; oncology; small animal; tumour biology.
© 2016 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
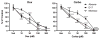

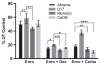
References
-
- Skorupski KA, Uhl JM, Szivek A, Allstadt Frazier SD, Rebhun RB, Rodriguez CO., Jr Carboplatin versus alternating carboplatin and doxorubicin for the adjuvant treatment of canine appendicular osteosarcoma: a randomized, phase III trial. Veterinary and Comparative Oncology. 2016;14:81–87. doi: 10.1111/vco.12069. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Somekh E, Douer D, Shaked N, Rubinstein E. In vitro effects of ciprofloxacin and pefloxacin on growth of normal human hematopoietic progenitor cells and on leukemic cell lines. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 1989;248:415–418. - PubMed
-
- Melo S, Villanueva A, Moutinho C, Davalos V, Spizzo R, Ivan C, et al. Small molecule enoxacin is a cancer-specific growth inhibitor that acts by enhancing TAR RNA-binding protein 2-mediated microRNA processing. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2011;108:4394–4399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1014720108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aranha O, Grignon R, Fernandes N, McDonnell TJ, Wood DP, Sarkar FH. Suppression of human prostate cancer cell growth by ciprofloxacin is associated with cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. International Journal of Oncology. 2003;22:787–794. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

